Loading...
These standards apply to riverine regulatory floodplains without a delineated floodway.
(A) The applicant shall obtain approval from IDNR-OWR for development of more than five acres or subdivisions of more than 50 lots located, entirely or partly, within the regulatory floodplain (without a delineated regulatory floodway).
(B) The development shall not singularly or cumulatively result in an obstruction of flood flows or potential flood damages outside the site due to an increase in flood heights, velocities or loss of floodplain area storage.
(C) If the riverine floodplain without a delineated floodway is in a Zone A with no BFEs shown, then a professional engineer shall submit a study that:
(1) Determines a BFE and demonstrates that the proposed development will maintain the existing conditions conveyance, will not increase flood velocities, will not increase flood profiles and will compensate for any lost floodplain storage in accordance with this subchapter; or
(2) Shows that the proposed development will meet the requirements for regulatory floodplains within this subchapter.
(Ord. 2019-03, passed 4-15-2019)
The following standards apply within the regulatory floodplain.
(A) Hydraulically equivalent compensatory storage volume will be required for development in a riverine regulatory floodplain, and shall be at least equal to the regulatory floodplain flood storage volume displaced, multiplied by one, within the incorporated areas. The storage volume displaced below the existing ten-year-frequency-flood elevation must be replaced below the proposed ten-year-frequency-flood elevation. The storage volume displaced above the existing ten-year-frequency flood elevation must be replaced above the proposed ten-year-frequency-flood elevation.
(B) Compensatory storage volume for development in a non-riverine regulatory floodplain area that is also adjacent to a lake shall be equal to the storage volume displaced.
(C) Compensatory storage volume requirements for development in a non-riverine regulatory floodplain that is not adjacent to a lake shall be replaced in accordance with the requirements for the loss of depressional storage as identified within this subchapter.
(D) Compensatory storage areas shall be designed to drain freely and openly to the channel, and shall be located adjacent to the development. This standard does not apply to non-riverine regulatory floodplain or the replacement of depressional storage.
(E) A recorded covenant running with the land shall be required to maintain the compensatory storage volume in areas modified to provide compensatory storage volume.
(Ord. 2019-03, passed 4-15-2019)
These standards are for the reconstruction, modification or new construction of bridges, culvert crossings and roadway approaches that are located within the regulatory floodplain.
(A) A proposed new structure shall not result in an increase of upstream flood stages greater than one-tenth foot, when compared to the existing conditions for all flood events, up to and including the base flood event, unless contained within the channel banks or recorded easements. The evaluation must be submitted to IDNR-OWR for review and issuance of a permit.
(B) If the proposed new structure will increase upstream flood stages greater than one-tenth foot, the applicant must contact IDNR-OWR for a dam safety permit or waiver. The Administrator shall be copied on all related correspondence.
(C) A restrictive bridge or culvert may be altered to increase the conveyance of the base flood, if an impact analysis is completed and approved in writing by the Administrator, and all other required regulatory approvals are obtained.
(D) Velocity increases must be mitigated by use of appropriate measures to avoid scour, erosion and sedimentation at the structure.
(Ord. 2019-03, passed 4-15-2019)
(A) Before any development in or near waters of the U.S., or in or near a wetland delineated on the NRCS Wetland Inventory Maps, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service National Wetland Inventory Map, or if the Administrator considers that a wetland is present through visual inspection, a written report identifying and evaluating the boundaries, location, limits, area and quality of all onsite wetlands shall be submitted. The presence and limits of wetland areas shall be determined by a wetland delineation conducted in accordance with the 1987 Corps of Engineers Wetland Delineation Manual. Before any development on agricultural land, in addition to the onsite delineation required under the provisions listed herein above, a farmed wetland delineation conducted in accordance with the National Food Security Act Manual methodology must be performed.
(B) The quality of the wetlands shall be evaluated based upon the Flora Quality Index (FQI).
(C) The approximate location, extent and relative quality of wetlands within 50 feet of the site shall be identified and included in the written report, if the wetland is downstream of the development such that the run off could negatively affect the quality or health of the wetland. The location and extent of such offsite wetlands shall be determined by using the first of the following documents or procedures pertaining to such wetlands at the time of development:
(1) Site-specific delineation;
(2) Wetlands identified in watershed plans or ADID studies. If such plans are not available, then;
(3) Wetlands identified in interim watershed plans. If such plans are not available, then;
(4) Wetlands identified on NRCS wetlands inventory maps. If such maps are not available, then;
(5) Wetlands identified on the United States Fish and Wildlife Service National Wetlands Inventory maps.
(D) Final FQI assessments made before June 1 or after October 15, unless allowed at the discretion of the Administrator, shall be considered to be preliminary. Buffer requirements shall be based upon such assessments.
(E) All wetland mitigation required under a COE Section 404 permit for wetland disturbances in the village, shall be provided for. All wetland mitigation required under this subchapter for wetland impacts in the village shall be provided for in the same watershed where the wetland disturbances occurred.
(Ord. 2019-03, passed 4-15-2019)
Preserved wetlands shall be protected during development such that an FQI calculated upon completion of the project or two years after the commencement of development, whichever is later, will not be more than two points less than the FQI originally calculated. The developer shall mitigate for any wetland not so preserved at the ratio required for in the FQI originally calculated.
(Ord. 2019-03, passed 4-15-2019)
The requirements of this section are not applicable to wetlands or waters of the U.S. that, in either case, are below the threshold-size limitations for mitigation requirements under the COE 404 permit program.
(A) Buffers shall be identified on development plans for all areas defined as waters of the U.S. Buffer areas are divided into two types: linear buffers and water body buffers.
(1) Buffer areas, including the protected waters of the U.S., shall be shown to be within appropriate easements on all new plats. Additionally, the maintenance requirements for the buffer shall be noted on the plat or included as a covenant running with the land in any deed conveying any portion of a buffer area.
(2) Buffer widths required as a part of a COE permit supersede the widths required in this section, unless the width required herein is greater. If a COE permit is obtained to permanently fill a portion of a wetland and no buffer is required, the buffer width required by this subchapter immediately adjacent to the area of impact does not apply. IMMEDIATELY ADJACENT refers to the area within 15 feet of the area of impact. In no case shall additional wetland area be filled to provide buffer required by this subchapter.
(3) Jurisdictional waters of the U.S. or wetlands may not constitute a buffer. Buffer widths are to be 25 feet unless otherwise determined using the criteria specified below. Buffer width averaging is acceptable at the discretion of the Administrator. When using buffer width averaging, the width may not be more than 20% less, at the narrowest point, than the specified width. The buffer width may never be less than 15 feet, except in the case of waters of the U.S. or wetlands with a calculated FQI of less than seven, where the buffer at its narrowest point may not be less than 12 feet in width.
(a) Linear buffers shall be designated along waters of the U.S. and wetlands associated with water courses, i.e., swales, creeks, streams, rivers, and the like. Refer to division (A)(3)(b) below in cases where wetlands are adjacent to and not part of the main channel, i.e., floodplain wetland, backwater slough, oxbow, bordering wetland complex.
1. When the lineal waters of the U.S. have a drainage area greater than 640 acres, measured at the downstream property line, or is designated as ADID because of high habitat value or an adjacent wetland has a calculated FQI greater than 16, the buffer shall be 50 feet.
2. When the lineal waters of the U.S. have a drainage area less than 640 acres, measured at the downstream property line, the buffer width shall be determined utilizing the formula,
X = (A*0.0547)+ 15
Where X equals the buffer width in feet, and A equals the drainage area in acres.
The width calculated by this formula shall be rounded up to the nearest multiple of five.
3. If protective measures are installed along the perimeter of a buffer, the width may be reduced by up to 10% immediately adjacent to the protective measure. The reduction in width that may be applied due to installation of protective measures may not be applied where buffer width averaging has been used and the buffer would be more than 20% less than originally specified. Protective measures may consist of fencing, sediment basins, biological filter strips or other methods approved by the Administrator.
4. If lineal waters of the U.S. are completely or partially relocated, the newly created portion must be constructed in a manner that will allow naturalizing to occur; for example, meandering, pools, riffles and the like. Additionally, all disturbed areas must be replanted for stability with native vegetation where appropriate, appropriately managed and maintained and protected by an appropriately-sized buffer.
(b) Water body buffers shall encompass non-linear bodies of water meeting the definition of the waters of the U.S., including wetlands.
1. If protective measures are installed along the perimeter of a buffer, the width may be reduced by up to 10% immediately adjacent to the protective measure. The reduction in width that may be applied due to installation of protective measures may not be applied where buffer width averaging has been used and the buffer would be more than 20% less than originally specified. Protective measures may consist of fencing, sediment basins, biological filter strips or other methods approved by the Administrator.
2. For all non-lineal water bodies or waters of the U.S. designated as ADID or wetlands with an FQI greater than 16, a minimum buffer width must be established in accordance with Table 1.
3. For non-ADID wetlands with an FQI of 7 to 16, a minimum buffer width must be established in accordance with Table 2.
4. For non-ADID wetlands with an FQI of less than 7, a minimum buffer width must be established in accordance with Table 3.
(B) Buffers shall be replanted or reseeded using appropriate predominately-native, deep-rooted vegetation, appropriately managed and maintained following disturbance.
(C) The buffer area for all lineal and non-lineal waters of the U.S., except wetlands, shall extend from the jurisdictional limits of the waters of the U.S. ordinary high water mark. The buffer area for wetlands shall extend from the edge of the approved delineated wetland boundary. A site may contain a buffer that originates from a waters of the U.S. or wetland located on another property.
(D) Constructed stormwater management features shall not require a buffer and may constitute as a buffer. The total width of the buffer required may not be reduced by the installation of a stormwater management facility unless the facility can be considered a protective measure. If the facility can be considered to be a protective measure, then the width of the buffer may be reduced as specified in this subchapter.
(E) If a buffer area is disturbed by permitted activities during construction, the buffer strip shall be stabilized in accordance with this subchapter.
(F) Access through buffer areas shall be allowed when necessary for maintenance purposes only. Unless otherwise dedicated for a public purpose, buffer areas shall remain private property and are not generally accessible to the public.
(G) Unrestrained stormwater that has not passed through a site runoff storage facility shall discharge through an area or structure meeting the definition of best management practices or buffer before entering the jurisdictional waters of the U.S. or a wetland.
(1) Once established, all buffer areas shall be maintained free from development, except as described below:
(a) A buffer area may be used for passive recreation (e.g., bird watching, walking, jogging, bicycling, horseback riding and picnicking), and it may contain pedestrian, bicycle or equestrian trails, provided that the created path is no wider than ten feet. To help prevent erosion, paths leading to a wetland must be winding.
(b) Utility maintenance, maintenance of drainage facilities and drainage easements shall be allowed, provided the maintenance activity meets all other federal, state and local regulations.
(c) Anchoring and placement of boat docks and piers shall be allowed, provided the structure meets all other federal, state and local regulations.
TABLE 1 – HIGH QUALITY WETLANDS – FQI > 16 | |||
Buffer Ratio | Wetland Area (Acres) | Buffer Area (Acres) | Buffer Width (Feet) |
0.5 | 0.25 | 0.125 | 15.0 |
0.5 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 20.0 |
0.5 | 0.75 | 0.375 | 25.0 |
0.5 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 30.0 |
0.5 | 1.25 | 0.625 | 30.0 |
0.5 | 1.5 | 0.75 | 35.0 |
0.5 | 1.75 | 0.875 | 35.0 |
0.5 | 2.0 | 1.0 | 40.0 |
0.5 | 2.25 | 1.125 | 40.0 |
0.5 | 2.5 | 1.25 | 45.0 |
0.5 | 2.75 | 1.375 | 45.0 |
0.5 | 3.0 | 1.5 | 50.0 |
0.5 | 3.25 | 1.625 | 50.0 |
0.5 | 3.5 | 1.75 | 50.0 |
0.5 | 3.75 | 1.875 | 50.0 |
0.5 | 4.0 | 2.0 | 50.0 |
0.5 | 4.25 | 2.125 | 50.0 |
0.5 | 4.5 | 2.25 | 50.0 |
0.5 | 4.75 | 2.375 | 50.0 |
0.5 | 5.0 or more | 2.5 | 50.0 |
Buffer ratio = % of total wetland area
Wetland Area = Total onsite and offsite area of the wetland
Buffer Area = Wetland Area x Buffer Ratio
Buffer Width = 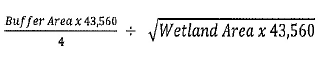
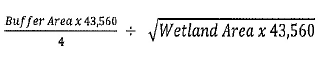
TABLE 2 – MEDIUM QUALITY WETLANDS – 7 < FQI < 16 | |||
Buffer Ratio | Wetland Area (Acres) | Buffer Area (Acres) | Buffer Width (Feet) |
0.4 | 0.25 | 0.1 | 15.0 |
0.4 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 15.0 |
0.4 | 0.75 | 0.3 | 20.0 |
0.4 | 1.0 | 0.4 | 25.0 |
0.4 | 1.25 | 0.5 | 25.0 |
0.4 | 1.5 | 0.6 | 30.0 |
0.4 | 1.75 | 0.7 | 30.0 |
0.4 | 2.0 | 0.8 | 30.0 |
0.4 | 2.25 | 0.9 | 35.0 |
0.4 | 2.5 | 1.0 | 35.0 |
0.4 | 2.75 | 1.1 | 35.0 |
0.4 | 3.0 | 1.2 | 40.0 |
0.4 | 3.25 | 1.3 | 40.0 |
0.4 | 3.5 | 1.4 | 40.0 |
0.4 | 3.75 | 1.5 | 45.0 |
0.4 | 4.0 | 1.6 | 45.0 |
0.4 | 4.25 | 1.7 | 45.0 |
0.4 | 4.5 | 1.8 | 45.0 |
0.4 | 4.75 | 1.9 | 50.0 |
0.4 | 5.0 or more | 2.0 | 50.0 |
Buffer ratio = % of total wetland area
Wetland Area = Total onsite and offsite area of the wetland
Buffer Area = Wetland Area x Buffer Ratio
Buffer Width =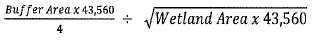
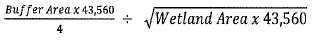
TABLE 3 – LOW QUALITY WETLANDS – FQI < 7 | |||
Buffer Ratio | Wetland Area (Acres) | Buffer Area (Acres) | Buffer Width (Feet) |
0.3 | 0.25 | 0.075 | 15.0 |
0.3 | 0.5 | 0.15 | 15.0 |
0.3 | 0.75 | 0.225 | 15.0 |
0.3 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 20.0 |
0.3 | 1.25 | 0.375 | 20.0 |
0.3 | 1.5 | 0.45 | 20.0 |
0.3 | 1.75 | 0.525 | 25.0 |
0.3 | 2.0 | 0.6 | 25.0 |
0.3 | 2.25 | 0.675 | 25.0 |
0.3 | 2.5 | 0.75 | 25.0 |
0.3 | 2.75 | 0.825 | 30.0 |
0.3 | 3.0 | 0.9 | 30.0 |
0.3 | 3.25 | 0.975 | 30.0 |
0.3 | 3.5 | 1.05 | 30.0 |
0.3 | 3.75 | 1.125 | 35.0 |
0.3 | 4.0 | 1.2 | 35.0 |
0.3 | 4.25 | 1.275 | 35.0 |
0.3 | 4.5 | 1.35 | 35.0 |
0.3 | 4.75 | 1.425 | 35.0 |
0.3 | 5.0 | 1.5 | 35.0 |
Buffer ratio = % of total wetland area
Wetland Area = Total onsite and offsite area of the wetland
Buffer Area = Wetland Area x Buffer Ratio
Buffer Width = 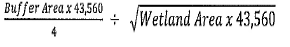
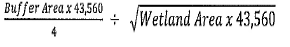
(Ord. 2019-03, passed 4-15-2019)
Loading...