Loading...
Upon either its own initiative or by application by an interested person, the Department may grant an exemption or variance request from any requirement in this Article if the Department finds that such exemption or variance will not result in an undue danger to life or property from radiation hazards. Any such application for modification and variance may be required to be supplemented and/or substantiated during Department review.
(Added City Record 4/24/2019, eff. 5/24/2019)
Notwithstanding anything to the contrary in this Code, the Department may:
(a) by rule, regulation, order, license condition or registration condition, or otherwise as appropriate, impose requirements upon any person subject to this Article, in addition to those expressly set forth in this Article, as it deems appropriate or necessary to protect the public health and safety and to minimize danger to life or property from radiation hazards;
(b) amend, suspend or revoke any license, registration or certified registration issued pursuant to this Article when it finds that any person holding such license, registration or certified registration is not in compliance with this Article, or other applicable laws, rules or regulations;
(c) by order, require the removal through an authorized person, or the surrender to the Department, of any radiation source by any person who:
(1) does not hold, or continue to hold, a valid license, registration or certified registration issued by the Department; or
(2) is not able or equipped, or who fails to observe with regard to such radiation source those radiation protection requirements of this Article, or who uses such radiation source in violation of this Article, Department order, or other applicable law, rule or regulation, or as set forth in a license, registration or certified registration issued by the Department. Upon such an order, such person shall be required to decontaminate any premises which may have been contaminated with radioactive material as a result of licensed or registered activities to radiation levels specified by the Department. Any expenses incidental to the transfer, surrender and decontamination shall be borne by the person responsible for the source.
(d) Except where the protection of the public health requires immediate action, no Department actions described in subdivisions (b) and (c) of this section shall take effect until the person so affected is given reasonable notice and an opportunity to be heard by the Department.
(Added City Record 4/24/2019, eff. 5/24/2019)
Part II: Radiation Equipment
"Absorbed dose (D)" means the energy imparted by ionizing radiation per unit mass of irradiated material. The SI unit of absorbed dose is joule per kilogram or gray (Gy). The previously used ("traditional") unit of absorbed dose is the rad (1 Gy = 100 rad).
"Absorbed dose rate" means absorbed dose per unit time, for machines with timers, or dose monitor unit per unit time for linear accelerators.
"Accelerator" means any machine capable of accelerating electrons, protons, or other charged particles in a vacuum and of discharging the resultant particulates or other radiation into a medium at energies usually in excess of 1 MeV.
"Accessible surface" means the external or outside surface of the enclosure or housing of the radiation producing machine as provided by the manufacturer. This includes the high-voltage generator, doors, access panels, latches, control knobs, and other permanently mounted hardware and including the plane across the exterior edge of any opening.
"Added filtration" means any filtration which is in addition to the inherent filtration.
"Air kerma (K)" means the kinetic energy released in air by ionizing radiation per mass of air. The SI unit of air kerma is joule per kilogram or gray (Gy).
"Air kerma rate (AKR)" means the air kerma per unit time.
"As low as reasonably achievable (ALARA)" means making every reasonable effort to maintain exposures to radiation as far below the dose limits in this Article as practical, consistent with the purpose for which the licensed or registered activity is undertaken, taking into account the state of technology, the economics of improvements in relation to the state of technology, the economics of improvements in relation to benefits to the public health and safety, and other societal and socioeconomic considerations in the public interest.
"Alert value" means a dose index (e.g., of CTDIvol (mGy) or DLP (mGy-cm)) that is set by the registrant to trigger an alert to the CT operator prior to scanning within an ongoing examination. The alert value represents a dose value well above the registrant's established range for the examination that warrants more stringent review and consideration before proceeding.
"Aluminum equivalent" means the thickness of type 1100 aluminum alloy affording the same attenuation, under specified conditions, as the material in question.
"Analytical x-ray equipment" means equipment that generates (by electronic means) and uses ionizing radiation for the purpose of examining the microstructure of materials, i.e. diffraction and spectroscopy (including fluorescence).
"Annual" means at least once per year, at about the same time each year, plus or minus one calendar month.
"Attenuation block" means a block or stack of type 1100 aluminum alloy, or aluminum alloy having equivalent attenuation, with dimensions 20 centimeters (cm) or larger by 20 cm or larger by 3.8 cm, that is large enough to intercept the entire x-ray beam.
"Authorized user" means a licensed physician who is identified as a user of therapeutic equipment on a certified registration issued by the Department.
"Automatic exposure control (AEC)" means a device which automatically controls one or more technique factors in order to obtain at a preselected location a required quantity of radiation.
"Automatic exposure rate control (AERC)" means a device which automatically controls one or more technique factors in order to obtain, at a preselected location, a required quantity of radiation per unit time.
"Background radiation" means radiation from cosmic sources; naturally occurring radioactive material, including radon (except as a decay product of source or special nuclear material); and global fallout as it exists in the environment from the testing of nuclear explosive devices or from past nuclear accidents such as Chernobyl that contribute to background radiation and are not under the control of the licensee or registrant. Background radiation does not include radiation from any regulated sources of radiation.
"Barrier" has the same meaning as "protective barrier."
"Beam axis" means a line from the source through the centers of the x-ray fields.
"Beam-limiting device" means a device which provides a means to restrict the dimensions of the x-ray field.
"Beam monitoring system" means a system designed and installed in the radiation head to detect and measure the radiation present in the useful beam.
"Beam scattering foil" means a thin piece of material, usually metallic, placed in the beam to scatter a beam of electrons in order to provide a more uniform electron distribution in the useful beam.
"Beam port" means an opening on the x-ray apparatus designed to emit a primary beam. This does not include openings on baggage units.
"Biennial" means the test is done at least once every other year, at about the same time, plus or minus one calendar month.
"Biweekly" means at least once per two consecutive weeks (see "Weekly").
"Bone densitometer" means a device intended for medical purposes to measure bone density and mineral content by x-ray or gamma ray transmission measurements through the bone and adjacent tissues. This generic type of device may include signal analysis and display equipment, patient and equipment supports, component parts, and accessories.
"Bone densitometry" means a noninvasive measurement of certain physical characteristics of bone that reflect bone strength. Test results are typically reported as bone mineral content or density and are used for diagnosing osteoporosis, estimating fracture risk, and monitoring changes in bone mineral content.
"C-arm fluoroscope" means a fluoroscopic x-ray system in which the image receptor and the x- ray tube housing assembly are connected or coordinated to maintain a spatial relationship. Such a system allows a change in the direction of the beam axis with respect to the patient without moving the patient.
"Calibration" means the determination of the response or reading of an instrument relative to a series of known radiation values over the range of the instrument, or the strength of a source of radiation relative to a standard.
"Cassette holder" means a device, other than a spot-film device, that supports or fixes the position of the cassette-based image receptor during a radiographic exposure.
"Cathode ray tube" means any device used to accelerate electrons for demonstration or research purposes, except where such cathode ray tube is incorporated into a television or display monitor that is subject to, and has met applicable federal radiation safety performance standards in 21 C.F.R. §§ 1010 and 1020.10.
"Certified Radiation Equipment Safety Officer" (CRESO) means an individual who holds an unexpired certificate as a radiation equipment safety officer issued by the New York State Department of Health.
"C.F.R." or "10 C.F.R." means, except where a citation to a specific section is given, the regulations issued by the United States Nuclear Regulatory Commission contained in Chapter I of Title 10 of the Code of Federal Regulations.
"Changeable filters" means any filter, exclusive of inherent filtration, which can be removed from the useful beam through any electronic, mechanical, or physical process.
"Coefficient of variation (C)" means the ratio of the standard deviation to the mean value of a population of observations. It is estimated using the following equation:

where:
s = Estimated standard deviation of the population.
x
i
= ith observation in sample;
n = Number of observations sampled.
"Collimator" means a device for restricting the useful radiation in one or more directions.
"Computed radiography (CR)" means a digital x-ray imaging method in which a photo-stimulable phosphor is used to capture and store a latent image. The latent image is read out by stimulating the phosphor with a laser. Computed radiography systems may use cassettes to house the phosphor, or it may be integrated into a digital radiography system. See also, the definition of "digital radiography."
"Computed tomography (CT)" means the production of a tomogram by the acquisition and computer processing of x-ray transmission data.
"Computed tomography dose index (CTDI)" means the average absorbed dose, along the z-axis, from a series of contiguous irradiations. It is measured from one axial CT scan (one rotation of the x-ray tube), and is calculated by dividing the integrated absorbed dose by the nominal total beam collimation. The scattering media for CTDI consist of two (16 and 32 cm in diameter) polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA, e.g., acrylic or Lucite) cylinders of 14 cm length. The equation is:

where:
D(z) = the radiation dose profile along the z-axis,
N = the number of tomographic sections imaged in a single axial scan. This is equal to the number of data channels used in a particular scan. The value of N may be less than or equal to the maximum number of data channels available on the system, and
T = the width of the tomographic section along the z-axis imaged by one data channel. In multiple-detector-row (multi-slice) CT scanners, several detector elements may be grouped together to form one data channel. In single-detector-row (single-slice) CT, the z-axis collimation (T) is the nominal scan width.
"Computed tomography (CT) scan" and "computerized axial tomography (CAT) scan" refer to an imaging procedure that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional images of the human body.
"Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT)" is a volumetric imaging modality. Volumetric data are acquired using two dimensional digital detector arrays and a cone-shaped x-ray beam (instead of fan-shaped) that rotates around the patient. Reconstruction algorithms can be used to generate images of any desired plane.
"Contact therapy system" means a therapeutic radiation machine with a short target to skin distance (TSD), usually less than 5 centimeters.
"Control panel" means that part of the x-ray control upon which are mounted the switches, knobs, pushbuttons, keypads, touchscreens, and other hardware necessary for manually setting the technique factors.
"Controlled area" has the same meaning as "restricted area".
"Conventional simulator" means any x-ray system designed to reproduce the geometric conditions of the radiation therapy equipment.
"Cradle" means a removable device which supports and may restrain a patient above an x-ray table; or a device whose patient support structure is interposed between the patient and the image receptor during normal use; or which is equipped with means for patient restraint and which is capable of rotation about its long (longitudinal) axis.
"CT conditions of operation" means all selectable parameters governing the operation of a CT x- ray system including nominal tomographic section thickness, filtration, and the technique factors as defined in this Article .
"CT dosimetry phantom" means the phantom used for determination of the dose delivered by a CT x-ray system. The phantom must be a right circular cylinder of polymethyl-methacrylate of density 1.19±0.01 grams per cubic centimeter. Except for pediatric dose measurements, the phantom must be at least 14 centimeters in length and must have diameters of 32.0 centimeters for testing any CT system designed to image any section of the body (whole body scanners) and 16.0 centimeters for any system designed to image the head (head scanners) or for any whole body scanner operated in the head scanning mode. The phantom must provide means for the placement of a dosimeter along its axis of rotation and along a line parallel to the axis of rotation 1.0 centimeter from the outer surface and within the phantom.
"CT number" means the number used to represent the x-ray attenuation associated with each elemental area of the CT image:
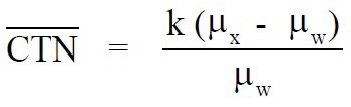
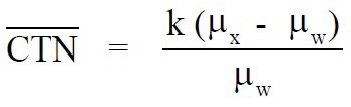
where:
k = A constant, a normal value of 1,000 when the Houndsfield scale of CT number is used;
µ
x
= Linear attenuation coefficient of the material of interest;
µ
w
= Linear attenuation coefficient of water.
"CTDI100" means the accumulated multiple scan dose at the center of a 100-mm scan and underestimates the accumulated dose for longer scan lengths. It is thus smaller than the equilibrium dose. The CTDI100 requires integration of the radiation dose profile from a single axial scan over specific integration limits. In the case of CTDI100, the integration limits are +50 mm, which corresponds to the 100-mm length of the commercially available "pencil" ionization chamber. CTDI100 is acquired using a 100-mm long, 3-cc active volume CT "pencil" ionization chamber and one of the two standard CTDI acrylic phantoms (16 and 32 cm diameter) and a stationary patient table. The equation is:

"CTDIvol" see "Volume Computed Tomography Dose Index (CTDIvol)"
"CTDIw" see "Weighted Computed Tomography Dose Index (CTDIw)"
"CT x-ray system" is technology that is used to perform CT scans and includes, but is not limited to: a control panel; image display device; gantry; x-ray tube; collimating device with filters; high voltage transformer; and, a data acquisition system. This includes CBCT systems that are used for other than dental x-ray scans.
"CT scanner" refers to technology used to perform and interpret CT scans and includes, but is not limited to: a control panel; gantry; high voltage generator; x-ray tube; table; and, display devices that are used for image interpretation.
"Cumulative air kerma" means the total air kerma accrued from the beginning of an examination or procedure and includes all contributions from fluoroscopic and radiographic irradiation.
"Dead-man switch" means a switch so constructed that a circuit closing contact can be maintained only by continuous pressure on the switch by the operator.
"Detector" has the same meaning as "radiation detector."
"Declared pregnant worker" means a worker who has voluntarily informed their employer, in writing, of their pregnancy and the estimated date of conception. The declaration remains in effect until the declared pregnant worker withdraws the declaration in writing or is no longer pregnant.
"Department" means the New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene.
"Diagnostic source assembly" means the tube housing assembly with a beam-limiting device attached.
"Diagnostic x-ray system" means an x-ray system designed for irradiation of any part of the human or animal body for the purpose of diagnosis or visualization.
"Diaphragm" means a device or mechanism by which the radiation beam is restricted in size.
"Digital radiography (DR)" means an x-ray imaging method or radiography which produces a digital rather than analog image. DR includes both computed radiography and direct digital radiography.
"Direct digital radiography (DDR)" means an x-ray imaging method in which a digital sensor, usually incorporating a thin-film transistor, is used to capture an x-ray image. Some DDR systems use a scintillator to convert x-rays to light and a photodiode array to convert light to charge, while others use a photoconductor to convert x-rays directly to charge, which is stored on the thin-film transistor. See also the definitions of "computed radiography" and "digital radiography."
"Direct scattered radiation" or "direct scatter radiation" means that scattered radiation which has been deviated in direction only by materials irradiated by the useful beam. See also the definition of "scattered radiation."
"Direct personal supervision" means that the qualified practitioner must be present in the room when the procedure is being performed and is immediately available to provide assistance and direction throughout the performance of the procedure.
"Direct supervision" means a qualified practitioner must exercise general supervision and be present in the facility and immediately available to furnish assistance and direction throughout the performance of the procedure. It does not mean that the qualified practitioner must be present in the room when the procedure is being performed.
"Dose" means the absorbed dose.
"Dose equivalent" means the product of the absorbed dose in tissue, quality factor, and all other necessary modifying factors, at the location of interest. Appropriate quality factors may be found in 10 C.F.R. § 20.2004.
"Dose area product (DAP) or "kerma-area product (KAP)" means the product of the air kerma and the area of the irradiated field and is typically expressed in Gy-cm
2
, so it does not change with distance from the x-ray tube.
"Dose length product (DLP)" means the indicator of the integrated radiation dose from a complete CT examination. It addresses the total scan length by the formula:
DLP (mGy-cm) = CTDIvol (mGy) x scan length (cm)
"Dose monitor unit (DMU)" means a unit response from the beam monitoring system from which the absorbed dose can be calculated.
"Dose profile" means the dose as a function of position along a line.
"Effective dose equivalent" is the sum of the products of the dose equivalent to the organ or tissue (HT) and the weighting factors (WT) applicable to each of the body organs or tissues that are irradiated: HE = Σ (WT HT).
"Electronic brachytherapy" means a method of radiation therapy where an electrically generated source of ionizing radiation is placed in or near the tumor or target tissue to deliver therapeutic radiation dosage.
"Electronic brachytherapy device" means the system used to produce and deliver therapeutic radiation including the x-ray tube, the control mechanism, the cooling system, and the power source.
"Electronic brachytherapy source" means the x-ray tube component used in an electronic brachytherapy device.
"Emergency procedure" means the written pre-planned steps to be taken in the event of actual or suspected exposure of an individual in excess of administrative or regulatory limits including the names and telephone numbers of individuals to be contacted.
"Equipment" means x-ray equipment, unless the specific context clearly indicates otherwise.
"Exposure rate" means exposure per unit of time, such as roentgen per minute. For purposes of this definition, "exposure" means the quotient dQ/dm, where dQ is the absolute value of the total charge of the ions of one sign produced in air and dm is the mass of air.
"External beam radiation therapy" means therapeutic irradiation in which the source of radiation is at a distance from the body.
"Extremity" means hand, elbow, arm below the elbow, foot, knee and leg below the knee.
"Facility" means the location, building, vehicle, or complex under one administrative control, at which one or more radiation machines are installed, located or used.
"Field of view (FOV)" means, in fluoroscopy, the diameter for circular image receptors or the diagonal for rectangular image receptors.
"Field emission equipment" means equipment which uses an x-ray tube in which electron emission from the cathode is due solely to the action of an electric field.
"Field-flattening filter" means a filter used to homogenize the absorbed dose rate over the radiation field.
"Filter" means material placed in the useful beam to preferentially absorb selected radiations.
"Fluoroscopic imaging assembly" means a subsystem in which x-ray photons produce a set of fluoroscopic images or radiographic images recorded from the fluoroscopic image receptor. It includes image receptors, electrical interlocks, if any, and structural material providing linkage between the image receptor and diagnostic source assembly.
"Fluoroscopic irradiation time" means the cumulative duration during an examination or procedure of operator-applied continuous pressure to the device, enabling x-ray tube activation in any fluoroscopic mode of operation.
"Fluoroscopically-Guided Interventional (FGI) procedures" means an interventional diagnostic or therapeutic procedure performed via percutaneous or other access routes, usually with local anesthesia or intravenous sedation, which uses external ionizing radiation in the form of fluoroscopy to localize or characterize a lesion, diagnostic site, or treatment site, to monitor the procedure, and to control and document therapy.
"Fluoroscopy" means a technique for generating x-ray images and presenting them simultaneously and continuously as visible images. This term has the same meaning as the term "radioscopy" in the standards of the International Electrotechnical Commission.
"Focal spot" means the area projected on the anode of the x-ray tube bombarded by the electrons accelerated from the cathode and from which the useful beam originates.
"Gantry" means that part of a radiation therapy system supporting and allowing movements of the radiation head about a center of rotation. For computed tomography, "gantry" means tube housing assemblies, beam-limiting devices, detectors, and the supporting structures, frames, and covers which hold or enclose these components within a computed tomography system.
"General purpose radiographic x-ray system" means any radiographic x-ray system which, by design, is not limited to radiographic examination of specific anatomical regions.
"General supervision" means the procedure is performed under the overall direction and control of the qualified practitioner but who is not necessarily required to be physically present during the performance of the procedure.
"Gonad shield" or "gonadal shield" means a protective barrier for the ovaries or testes.
"Gray (Gy)" means the SI unit of absorbed dose, kerma, and specific energy imparted equal to 1 joule per kilogram. Also see "Absorbed Dose".
"Half-value layer (HVL)" means the thickness of specified material which attenuates the beam of radiation to an extent such that the AKR is reduced by one-half of its original value. For the purposes of this definition, the contribution of all scattered radiation, other than any which might be present initially in the beam concerned, is deemed to be excluded.
"Hand-held x-ray equipment" or "hand-held x-ray system" means x-ray equipment that is designed to be hand-held during operation.
"Healing arts" means the use of radiation for purposes of medical diagnosis or treatment of humans or animals.
"Healing arts screening" means the testing of human beings using x-ray machines for the detection or evaluation of health indications when such tests are not specifically and individually ordered by a licensed practitioner of the healing arts legally authorized to prescribe such x-ray tests for the purpose of diagnosis or treatment.
"Image intensifier" means a device, installed in its housing, which instantaneously converts an x- ray pattern, in an analog fashion, into a corresponding light image of higher intensity.
"Image receptor" means any device, such as a fluorescent screen, radiographic film, x-ray image intensifier tube, solid-state detector, or gaseous detector which transforms incident x-ray photons either into a visible image or into another form which can be made into a visible image by further transformations. In those cases where means are provided to preselect a portion of the image receptor, the term "image receptor" shall mean the preselected portion of the device.
"Individual monitoring devices" ""means devices designed to be worn by a single individual for the assessment of effective dose equivalent, such as film badges, thermo-luminescent dosimeters (TLDs), optically-stimulated luminescent dosimeters (OSLDs), pocket ionization chambers etc.
"Inherent filtration" means the filtration of the useful beam provided by the permanently installed components of the tube housing assembly.
"Inspection" means an official examination or facility observation including, but not limited to, reviews of tests, reports, assessments, specifications, surveys and monitoring to determine compliance with applicable rules, regulations, orders, requirements and conditions enforceable by the Department.
"Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT)" means radiation therapy that uses non-uniform radiation beam intensities which have been determined by various computer-based optimization techniques.
"Interlock" means a device or engineered system that precludes access to an area of radiation hazard either by preventing entry or by automatically removing the hazard.
"Interruption of irradiation" means the stopping of irradiation with the possibility of continuing irradiation without resetting of operating conditions at the control panel.
"Irradiation" means the exposure of matter to ionizing radiation.
"Isocenter" means the center of the smallest sphere through which the beam axis passes when the equipment moves through a full range of rotations about its common center.
"Kerma" means the quantity defined by the International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements. The kerma, K, is the quotient of dEtr by dm, where dEtr is the sum of the initial kinetic energies of all the charged particles liberated by uncharged particles in a mass dm of material; thus K=dEtr/dm, in units of J/kg, where the special name for the unit of kerma is gray (Gy). When the material is air, the quantity is referred to as "air kerma." "Kerma-area product (KAP)" has the same meaning as "dose area product."
"Kilovolt (kV)" or "(kilo electron volt (keV))" means the energy equal to that acquired by a particle with one electron charge in passing through a potential difference of 1,000 volts in a vacuum. (Note: current convention is to use kV for photons and keV for electrons.)
"Kilovolt peak (kVp)" means the maximum value in kilovolts of the potential difference of a pulsating generator. When only one-half of the wave is used, the value refers to the useful half of the wave.
"kWs" means kilowatt second.
"Last-image hold (LIH) radiograph" means an image obtained either by retaining one or more fluoroscopic images, which may be temporarily integrated, at the end of a fluoroscopic exposure or by initiating a separate and distinct radiographic exposure automatically and immediately in conjunction with termination of the fluoroscopic exposure.
"Lead equivalent" means the thickness of lead affording the same attenuation, under specified conditions, as the material in question.
"Leakage radiation" means all radiation coming from within the source housing, except the useful beam or radiation produced when the exposure switch or timer is not activated.
"Leakage technique factors" means the technique factors associated with the diagnostic source assembly which are used in measuring leakage radiation and defined as follows:
(a) For diagnostic source assemblies intended for capacitor energy storage equipment, the maximum-rated peak tube potential and the maximum-rated number of exposures in an hour for operation at the maximum-rated peak tube potential with the quantity of charge per exposure being 10 millicoulombs (or 10 mAs) or the minimum obtainable from the unit, whichever is larger;
(b) For diagnostic source assemblies intended for field emission equipment rated for pulsed operation, the maximum-rated peak tube potential and the maximum-rated number of x- ray pulses in an hour for operation at the maximum-rated peak tube potential; and
(c) For all other diagnostic source assemblies, the maximum-rated peak tube potential and the maximum-rated continuous tube current for the maximum-rated peak tube potential.
"Licensed radiologic technologist (LRT)" means an individual who is licensed and operates in compliance with Article 35 of the New York State Public Health Law and Part 89 of Title 10 of the New York Articles, Rules and Regulations, or any successor law or regulations.
"Licensee" means any person who is licensed by the Department in accordance with this Article or any person who possesses radioactive material which is subject to the licensure requirements of this Article.
"Light field" means that area of the intersection of the light beam from the beam-limiting device and one of the set of planes parallel to and including the plane of the image receptor, whose perimeter is the locus of points at which the illumination visually appears to be approximately one-fourth of the maximum in the intersection.
"Limited-use system" means a personnel screening system that is capable of delivering an effective dose equivalent greater than 0.25 µSv (25 µrem) per screening but cannot exceed an effective dose equivalent of 10 µSv (1 mrem) per screening. Limited-use systems require additional controls and documentation to ensure that annual individual dose limits required by H.12e. appropriate regulations or national standards are not exceeded.
"Line-voltage regulation" means the difference between the no-load and the load line potentials expressed as a percent of the load line potential:
Percent line-voltage regulation = 100 (V
n
- V
l
) / V
l
)
where:
V
n
= No-load line potential; and
V
l
= Load line potential.
"mA" means milliampere.
"mAs" means milliampere second.
"Medical event" means a situation (except for an event that results from patient intervention) in which the administration of radiation from any radiation source results in:
(a) a dose that differs from the prescribed dose by more than 0.05 Sv (5 rem) effective dose equivalent, 0.5 Sv (50 rem) to an organ or tissue, or 0.5 Sv (50 rem) shallow dose equivalent to the skin; and
(1) the total dose delivered differs from the prescribed dose by 20 percent or more; or
(2) the fractionated dose delivered differs from the prescribed dose, for a single fraction, by 50 percent or more.
(b) a dose that exceeds 0.05 Sv (5 rem) effective dose equivalent, 0.5 Sv (50 rem) to an organ or tissue, or 0.5 Sv (50 rem) shallow dose equivalent to the skin from any of the following:
(1) an administration of a dose to the wrong individual or human research subject;
(2) an administration of a dose delivered by the wrong mode of treatment.
(c) a dose to the skin or an organ or tissue other than the treatment site that exceeds by 0.5 Sv (50 rem) to an organ or tissue and 50 percent or more of the dose expected from the administration defined in the written directive;
(d) the administration of a CT or CBCT scan in which any of the following occur:
(1) a CT or CBCT scan is performed on the wrong person;
(2) a CT or CBCT scan is performed on the wrong body part, such that the patient dose from the scan to the wrong body part results in an effective dose equivalent exceeding 2.5 mSv (250 mrem), or 50 mSv (5 rem) to an organ or tissue;
(3) a CT or CBCT scan that results in damage to an organ, organ system or results in hair loss or erythema as determined by a physician; or
(e) Any event resulting from intervention of a patient or human research subject in which the radiation from any radiation source results or will result in unintended permanent functional damage to an organ or a physiological system, as determined by a physician.
"Medical institution" means a "hospital" as defined in New York State Public Health Law § 2801(1).
"Megavolt (MV)" or "mega electron volt (MeV)" means the energy equal to that acquired by a particle with one electron charge in passing through a potential difference of 1,000,000 volts in a vacuum. (Note: current convention is to use MV for photons and MeV for electrons.)
"Minor" means an individual less than 18 years of age.
"Mobile electronic brachytherapy service" means transportation of an electronic brachytherapy device to provide electronic brachytherapy at an address that is not the address of record.
"Mobile x-ray equipment" has the meaning ascribed to it in the definition of "x-ray equipment."
"Mode of operation" means, for fluoroscopic systems, a distinct method of fluoroscopy or radiography provided by the manufacturer and selected with a set of several technique factors or other control settings uniquely associated with the mode. The set of distinct technique factors and control settings for the mode may be selected by the operation of a single control. Examples of distinct modes of operation include normal fluoroscopy (analog or digital), high-level control fluoroscopy, cineradiography (analog and digital), digital subtraction angiography, electronic radiography using the fluoroscopic image receptor, and spot film recording. In a specific mode of operation, certain system variables affecting kerma, AKR, or image quality, such as image magnification, x-ray field size, pulse rate, pulse duration, number of pulses, source-image receptor distance (SID), or optical aperture, may be adjustable or may vary; their variation per se does not comprise a mode of operation different from the one that has been selected.
"Monitor unit (MU)" has the same meaning as "dose monitor unit."
"Monthly" means at least once per calendar month.
"Moving beam radiation therapy" means radiation therapy with any planned displacement of radiation field or patient relative to each other, or with any planned change of absorbed dose distribution. It includes arc, skip, conformal, intensity modulation and rotational therapy.
"Noise" in CT means the standard deviation of the fluctuations in CT number expressed as a percentage of the attenuation coefficient of water. Its estimate (Sn) is calculated using the following expression:

where:
CS = Linear attenuation coefficient of the material of interest.
µ
W
= Linear attenuation coefficient of water.
s = Estimated [S]standard deviation of the CT numbers of picture elements in a specified area of the CT image.
"Nominal tomographic section thickness" means the full width at half-maximum of the sensitivity profile taken at the center of the cross-sectional volume over which x-ray transmission data are collected.
"Nominal treatment distance" means:
(a) for electron irradiation, the distance from the scattering foil, virtual source, or exit window of the electron beam to the entrance surface of the irradiated object along the central axis of the useful beam.
(b) for x-ray irradiation, the virtual source or target to isocenter distance along the central axis of the useful beam. For non-isocentric equipment, this distance shall be that specified by the manufacturer.
"Normal operating procedures" mean step-by-step instructions necessary to accomplish the task. These procedures may include sample insertion and manipulation, equipment alignment, routine maintenance by the registrant, and data recording procedures, which are related to radiation safety.
"Occupational dose" means the dose received by an individual in the course of employment in which the individual's assigned duties involve exposure to radiation or to radioactive material from licensed and unlicensed sources of radiation, whether in the possession of the licensee, registrant, or other person. Occupational dose does not include doses received from background radiation, from any medical administration the individual has received, from exposure to individuals administered radioactive material or implants and released from voluntary participation in medical research programs, or as a member of the public.
"Open-beam x-ray equipment" means an x-ray system in which the beam path could be entered by any part of the body at any time.
"Patient" means an individual or animal subjected to healing arts examination, diagnosis or treatment or machine-produced radiation for the purposes of medical therapy.
"Patient intervention" means actions by the patient or human research subject, whether intentional or unintentional, such as dislodging or removing treatment devices or prematurely terminating the administration.
"Peak tube potential" means the maximum value of the potential difference across the x-ray tube during an exposure.
"Periodic quality assurance check" means a procedure which is performed to ensure that a previous parameter or condition continues to be valid.
"Personal supervision" means a qualified practitioner must exercise "general supervision" (as defined in this Article) and be present in the room or adjacent control area during the performance of the procedure.
"PBL" (See "Positive beam limitation").
"Person" means, notwithstanding 24 RCNY Health Code § 1.03, any individual, corporation, partnership, firm, association, trust, estate, public or private institution, group, agency, political subdivision of this State, any other State or political subdivision or agency thereof, and any legal successor, representative, agent, or agency of the foregoing. For purposes of entities other than individual professional practitioners applying to this Department for the issuance of a radiation equipment registration or radioactive materials license, "person" shall mean only a principal officer, director or executive of the applying entity with authority to legally bind the applying entity to the obligations attendant to such registration or license.
"Phantom" means a test object either used to determine system characteristics or to evaluate system performance. The composition and design of a phantom varies based on the modality and test it is used for.
"Photostimulable storage phosphor (PSP)" means a material used to capture and store radiographic images in computed radiography systems.
"Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS)" is a medical imaging technology that provides access to and storage for medical images from multiple modalities. It is comprised of an image acquisition system, display, network and data storage or archiving system.
"Picture element" means an elemental area of a tomogram.
"PID" has the same meaning as "position indicating device".
"Pitch" means the table incrementation, per x-ray tube rotation, divided by the nominal x-ray beam width at isocenter.
"Portable x-ray equipment" has the meaning ascribed to it in the definition of "x-ray equipment."
"Position indicating device (PID)" means a device on dental x-ray equipment used to indicate the beam position and to establish a definite source-surface (skin) distance. It may or may not incorporate or serve as a beam-limiting device.
"Positive beam limitation" means the automatic or semi-automatic adjustment of an x-ray beam to the size of the selected image receptor, whereby exposures cannot be made without such adjustment.
"Prescribed dose" means the total dose and dose per fraction as documented in the written directive by a medical doctor.
"Primary beam" means the ionizing radiation coming directly from the radiation source through a beam port into the volume defined by the collimation system.
"Primary dose monitoring system" means a system which will monitor the useful beam during irradiation and which will terminate irradiation when a pre-selected number of dose monitor units have been delivered.
"Primary protective barrier" see "Protective barrier"
"Professional practice" means the practice of medicine, dentistry, podiatry, osteopathy, chiropractic or veterinary medicine.
"Professional practitioner" means any person licensed or otherwise authorized under the Education Law to operate a professional practice.
"Protective barrier" means a barrier of radiation absorbing material used to reduce radiation exposure. The types of protective barriers are:
(a) "primary protective barrier" or "primary barrier" means the material, excluding filters, placed in the useful beam.
(b) "secondary protective barrier" or "secondary barrier" means the material which attenuates stray radiation.
"Protective garment" means an apron, glove, thyroid shield or other protective barrier worn by a professional practitioner or licensed radiographic technologist or patient made of radiation attenuating material, used to reduce radiation exposure.
"Protocol" means a collection of settings and parameters that fully describe an examination.
"Pulsed mode" means operation of the x-ray system such that the x-ray tube current is pulsed by the x-ray control to produce one or more exposure intervals of duration less than one-half second.
"Qualified Medical Physicist (QMP)" means an individual who:
(a) is licensed and maintains a current registration in accordance with Article 166 of the New York State Education Law and applicable regulations to practice any subspecialty of medical physics; and
(b) for certified registrations, is listed on the certified registration and has been granted certification in a specific subfield of medical physics by an appropriate national certifying body and abides by the certifying body's requirements for continuing education.
"Quality Assurance (QA)" means a program providing for verification by written procedures, such as testing, auditing and inspection, to ensure that deficiencies, deviations, defective equipment, unsafe practices, or a combination thereof, relating to the use, disposal, management, or manufacture of radiation equipment or radioactive material, are identified, promptly corrected and reported to the appropriate regulatory authorities as required.
"Quarterly" means an activity is done at least once in every third month, before the last business day or the end of the month, whichever comes first.
"Rad" means the special unit of absorbed dose. One rad is equal to an absorbed dose of 100 ergs per gram or 0.01 joule per kilogram (0.01 gray).
"Radiation" means alpha particles, beta particles, gamma rays, x rays, neutrons, high-speed electrons, high-speed protons, and other particles capable of producing ions. For purposes of this Article, ionizing radiation is an equivalent term. As used in this Article, radiation does not include non-ionizing radiation, such as radiowaves or microwaves, visible, infrared or ultraviolet light.
"Radiation detector" means a device which in the presence of radiation provides a signal or other indication suitable for use in measuring one or more quantities of incident radiation.
"Radiation head" means the structure from which the useful beam emerges.
"Radiation installation" means any location of radiation-producing equipment subject to this Article.
"Radiation Protocol Committee (RPC)" means the representative group of qualified individuals in a CT or FGI facility responsible for the ongoing review and management of CT or FGI protocols to ensure that exams being performed achieve the desired diagnostic image quality at the lowest radiation dose possible while properly exploiting the capabilities of the equipment being used. This committee and these functions may be subsumed under the registrant's radiation safety committee as described in 24 RCNY Health Code § 175.09(e).
"Radiation safety officer (RSO)" means an individual described in 24 RCNY Health Code § 175.10.
"Radiation source" means any radioactive material or any radiation equipment.
"Radiation source housing" or "x-ray tube housing" means that portion of an x-ray system which contains the x-ray tube or secondary target. Often the housing contains radiation shielding material or inherently provides shielding.
"Radiation therapy simulation system" means a radiographic or fluoroscopic x-ray system intended for localizing the volume to be exposed during radiation therapy and confirming the position and size of the therapeutic irradiation field.
"Radioactive material" means any solid, liquid or gas which emits radiation spontaneously.
"Radiograph" means an image receptor on which the image is created directly or indirectly by an x-ray pattern and results in a permanent record, permanent film or a digital image produced on a sensitive surface by a form of radiation other than direct visible light.
"Radiography" means a technique for generating and recording an x-ray pattern for the purpose of providing the user with an image after termination of the exposure; the process of creating radiographic images.
"Recording" means producing a retrievable form of an image resulting from x-ray photons.
"Redundant beam monitoring system" means a combination of two independent dose monitoring systems in which each system is designed to terminate irradiation in accordance with a pre- selected number of dose monitor units.
"Reference level" means dose levels in medical radio-diagnostic practices for typical examinations for groups of standard-sized patients or standard phantoms for broadly defined types of equipment.
"Registrant" means an individual or entity issued a certificate of registration, or certified registration, from the Department to operate registered radiation equipment.
"Rem" means the special unit of any of the quantities expressed as dose equivalent. The dose equivalent in rem is equal to the absorbed dose in rad multiplied by the quality factor. One rem is equal to 0.01 sievert.
"Roentgen (R)" Means the special unit of exposure. One roentgen equals 2.58E-4 coulomb per kilogram of air.
"Restricted area" means an area, access to which is limited for the purpose of protecting individuals against undue risks from exposure to sources of radiation. A restricted area does not include any area used as residential quarters (but separate rooms in a residential building may be set apart as a restricted area).
"Safety device" means a device, interlock or system that prevents the entry of any portion of an individual's body into the primary x-ray beam or that causes the beam to shut off upon entry into its path.
"Scan" means the complete process of collecting x-ray transmission data for the production of a tomogram. Data may be collected simultaneously during a single scan for the production of one or more tomograms.
"Scan increment" means the amount of relative displacement of the patient with respect to the CT x-ray system between successive scans measured along the direction of such displacement.
"Scan sequence" means a pre-selected set of two or more scans performed consecutively under pre-selected CT conditions of operation.
"Scan time" means the time elapsed during the accumulation of x-ray transmission data for a single scan.
"Scattered radiation" or "scatter radiation" means radiation that has been deviated in direction or energy by passing through matter.
"Screening" means the application of x-ray radiation to diagnose a particular condition, as in the application of mammography x-rays to a female population to diagnosis the incidence of breast cancer.
"Sealed x-ray units" means any x-ray unit to which the Department affixes warning labels to in order to notify the registrant that the x-ray unit shall not be used for clinical x-ray exams.
"Secondary dose monitoring system" means a system which will terminate irradiation in the event of failure of the primary dose monitoring system.
"Semi-annual" means an activity is performed once within every sixth month before the end of the last business day or the end of the month, whichever comes first.
"Sensitivity profile" means the relative response of the CT x-ray system as a function of position along a line perpendicular to the tomographic plane.
"Shutter" means a moveable device attached to the tube housing assembly which can intercept the entire cross sectional area of the useful beam and which has a lead equivalency not less than that of the tube housing assembly and is used to block the useful or primary beam emitted from an x-ray tube assembly.
"SI" means the International System of Units, usually abbreviated "SI" and refers to the modern metric system of measurement.
"SID" has the same meaning as "source-image receptor distance."
"Sievert (Sv)" means the SI unit of dose equivalent. The unit of dose equivalent is the joule per kilogram. The previously used ("traditional") unit of dose equivalent is the rem. (1 Sv=100 rem).
"Simulator (radiation therapy simulation system)" means any x-ray system intended for localizing the volume to be exposed during radiation therapy and establishing the position and size of the therapeutic irradiation field. See also the definitions of conventional simulator" and "virtual simulator."
"Skyshine" means radiation, such as neutrons and photons, generated by high energy proton accelerators over 10 MeV, which can be scattered by the atmosphere near the facility and result in public exposure as a scattered dose.
"Source" means the region or material from which the radiation emanates, for example, the focal spot of an x-ray tube.
"Source-image receptor distance (SID)" means the distance from the source to the center of the input surface of the image receptor.
"Source-skin distance (SSD)" means the distance from the source to the center of the entrant x- ray field in the plane tangent to the patient skin surface.
"Spot-film" means a cassette-based radiograph which is made during a fluoroscopic examination to permanently record a relevant image visible during that fluoroscopic procedure.
"Spot-film device" means a device intended to transport or position a radiographic image receptor between the x-ray source and fluoroscopic image receptor. It includes a device intended to hold a cassette over the input end of the fluoroscopic image receptor for the purpose of producing a radiograph.
"Stationary beam radiation therapy" means radiation therapy without displacement of one or more mechanical axes relative to the patient during irradiation.
"Storage" means a condition in which a device or source is not being used for an extended period of time, and has been made inoperable.
"Stray radiation" means the sum of leakage and scatter radiation.
"Substantial radiation dose level (SRDL)" means an appropriately-selected dose used to trigger additional dose-management actions during a procedure and medical follow-up for a radiation level that might produce a clinically-relevant injury in an average patient.
"Target" means that part of an x-ray tube or accelerator onto which a beam of accelerated particles is directed to produce ionizing radiation or other particles.
"Target-skin distance (TSD)" means the distance measured along the beam axis from the center of the front surface of the x-ray target or electron virtual source to the surface of the irradiated object or patient.
"Technique" means the settings selected on the control panel of the equipment.
"Technique chart" means a chart that lists the standard settings and positions for a given technique.
"Technique factors" means the conditions of operation displayed by the x-ray equipment, such as:
(a) for capacitor energy storage equipment, peak tube potential in kilovolts (kV) and quantity of charge in milliampere-seconds (mAs);
(b) for field emission equipment rated for pulsed operation, peak tube potential in kV, and number of x-ray pulses;
(c) for CT equipment designed for pulsed operation, peak tube potential in kV, scan time in seconds, and either tube current in milliamperes (mA), x-ray pulse width in seconds, and the number of x-ray pulses per scan, or the product of tube current, x-ray pulse width, and the number of x-ray pulses in mAs;
(d) for CT equipment not designed for pulsed operation, peak tube potential in kV, and either tube current in mA and scan time in seconds, or the product of tube current and exposure time in mAs and the scan time when the scan time and exposure time are equivalent. Based on the manufacturer, the time-current product may be scaled by other scan parameters like the pitch; and
(e) for all other equipment, peak tube potential in kV, and either tube current in mA and exposure time in seconds, or the product of tube current and exposure time in mAs.
"Tenth-value layer (TVL)" means the thickness of a specified material which attenuates x- radiation or gamma radiation to an extent such that the air kerma rate, exposure rate, or absorbed dose rate is reduced to one-tenth of the value measured without the material at the same point.
"Termination of irradiation" means the stopping of irradiation in a fashion which will not permit continuance of irradiation without the resetting of operating conditions at the control panel.
"Test" means the process of verifying compliance with an applicable standard or requirement.
"Therapeutic radiation machine" means photon or charged particle-producing equipment designed and used for external beam radiation therapy. For purposes of this Article, devices used to administer electronic brachytherapy or superficial photon or charged particle therapy shall also be considered therapeutic radiation machines.
"This Article" means 24 RCNY Health Code Article 175 and all other parts of the New York City Health Code applicable to licensees and registrants or other persons subject to the provisions of 24 RCNY Health Code Article 175, including but not limited to 24 RCNY Health Code Articles 1, 3 and 5.
"Tomogram" means the depiction of the x-ray attenuation properties of a section through the body.
"Tomographic plane" means that geometric plane which the manufacturer identified as corresponding to the output tomogram.
"Tomographic section" means the volume of an object whose x-ray attenuation properties are imaged in a tomogram.
"Total Effective Dose Equivalent (TEDE)" means the sum of the effective dose equivalent (for external exposures) and the committed effective dose equivalent (for internal exposures; committed effective dose equivalent is a measure of dose that will be received from intake of radioactive material).
"Tube" means an x-ray tube, unless otherwise specified.
"Tube housing assembly" means the tube housing with tube installed. It includes high-voltage or filament transformers and other appropriate elements when such are contained within the tube housing.
"Unintended" radiation dose in diagnostic or interventional x-ray means a patient radiation dose resulting from a human error or equipment malfunction during the procedure.
"Useful beam" means the radiation which passes through the tube housing port and the aperture of the beam limiting device when the exposure switch or timer is activated to cause the radiation machine to produce radiation.
"Virtual simulator" means a computed tomography (CT) unit used in conjunction with relevant software which recreates the treatment machine; and that allows import, manipulation, display, and storage of images from CT or other imaging modalities.
"Virtual source" means a point from which radiation appears to originate.
"Visible area" means that portion of the input surface of the image receptor over which incident x-ray photons are producing a visible image.
"Volume Computed Tomography Dose Index (CTDIvol)" means a radiation dose parameter derived from the CTDIw (weighted or average CTDI given across the field of view). The formula is:
CTDIvol = (N)(T)(CTDIw)/I
where:
N = number of simultaneous axial scans per x-ray source rotation,
T = thickness of one axial scan (mm), and
I = table increment per axial scan (mm).
Thus,
CTDIvol = CTDIw / pitch
"Warning device" means a visible or audible signal that warns individuals of a potential radiation hazard.
"Wedge filter" means a filter which effects continuous change in transmission over all or a part of the useful beam.
"Weighting factor WT" for an organ or tissue (T) means the proportion of the risk of stochastic effects resulting from irradiation of that organ or tissue to the total risk of stochastic effects when the whole body is irradiated uniformly. For calculating the effective dose equivalent, the values of WT are:
Organ Dose Weighing Factors | |
Organ or Tissue | WT |
Organ Dose Weighing Factors | |
Organ or Tissue | WT |
Gonads | 0.25 |
Breast | 0.15 |
Red bone marrow | 0.12 |
Lung | 0.12 |
Thyroid | 0.03 |
Bone surfaces | 0.03 |
Remainder | 0.30 1 |
Whole body | 1.00 2 |
1 0.30 results from 0.06 for each of 5 "remainder" organs, excluding the skin and the lens of the eye, that receive the highest doses.
2 For the purpose of weighting the external whole body dose, for adding it to the internal dose, a single weighting factor, WT = 1.0, has been specified. The use of other weighting factors for external exposure will be approved on a case-by-case basis until such time as specific guidance is issued.
"Weekly" means at least once per week, where a week means seven consecutive days starting on Sunday.
"Whole body" means, for purposes of external exposure, head, trunk (including male gonads), arms above the elbow, or legs above the knee.
"Written directive" means an order in writing for the administration of radiation to a specific patient or human research subject.
"Weighted Computed Tomography Dose Index (CTDIw)" means the estimated average CTDI100 across the field of view (FOV). The equation is:
CTDIw = 1/3(CTDI100, center) + 2/3(CTDI100, edge)
where, 1/3 and 2/3 approximate the relative areas represented by the center and edge values derived using the 16 or 32 cm acrylic phantom. CTDIw uses CTDI100 and an f-factor for air (0.87 rad/R or 1.0 mGy/mGy).
"X-ray control" means a device which controls input power to the x-ray high-voltage generator or the x-ray tube. It includes equipment such as timers, phototimers, automatic brightness stabilizers, and similar devices, which control the technique factors of an x-ray exposure.
"X-ray exposure control" means a device, switch, button or other similar means by which an operator initiates or terminates the radiation exposure. The x-ray exposure control may include such associated equipment as timers and back-up timers.
"X-ray equipment" means an x-ray system, subsystem, or component thereof. Types of x-ray equipment are as follows:
(a) "mobile x-ray equipment" means x-ray equipment mounted on a permanent base with wheels or casters for moving while completely assembled.
(b) "portable x-ray equipment" means x-ray equipment designed to be hand-carried.
(c) "stationary x-ray equipment" means x-ray equipment which is installed in a fixed location. (d) "hand-held x-ray equipment" means x-ray equipment that is designed to be hand- held during operation.
"X-ray field" means that area of the intersection of the useful beam and any one of a set of planes parallel to and including the plane of the image receptor, whose perimeter is the locus of points at which the AKR is one-fourth of the maximum in the intersection. On recording devices that visualize the x-ray field, the perimeter can be taken to be the locus of points at which the brightness as it visually appears to the observer is approximately one-fourth of the maximum brightness in the intersection.
"X-ray high-voltage generator" or "x-ray generator" means a device which transforms electrical energy from the potential supplied by the x-ray control to the tube operating potential. The device may also include means for transforming alternating current to direct current, filament transformers for the x-ray tube, high-voltage switches, electrical protective devices, and other appropriate elements.
"X-ray system" means an assemblage of components for the controlled production of x-rays. It includes minimally an x-ray high-voltage generator, an x-ray control, a tube housing assembly, a beam-limiting device, and the necessary supporting structures. Additional components which function with the system are considered integral parts of the system.
"X-ray table" means a patient support device with its patient support structure (tabletop) interposed between the patient and the image receptor during radiography or fluoroscopy. This includes, but is not limited to, any stretcher equipped with a radiolucent panel and any table equipped with a cassette tray (or bucky), cassette tunnel, fluoroscopic image receptor, or spot- film device beneath the tabletop.
"X-ray tube" means any electron tube which is designed for the conversion of electrical energy into x-ray energy.
(Added City Record 4/24/2019, eff. 5/24/2019)
Each registrant must at a minimum:
(a) develop, document and implement a radiation protection program commensurate with the scope and extent of their operations and sufficient to ensure compliance with the provisions of this Article. The radiation safety program must include, but not be limited to, the following policies, procedures and activities:
(1) that the use of ionizing radiation within its purview is performed in accordance with existing laws and regulations; this requirement shall be deemed to be met by the registrant possessing a Quality Assurance Manual in accordance with 24 RCNY Health Code § 175.12 for the facility.
(2) that all persons are protected from radiation as required by this Article. A current and readily-accessible copy of 24 RCNY Health Code Article 175 must be maintained by the registrant at the facility either in hard copy or electronic format.
(b) use, to the extent practical, procedures and engineering controls based upon 'best practice' radiation protection principles to achieve occupational doses and doses to members of the public that are as low as reasonably achievable (ALARA) below the limits specified in this Article.
(c) provide a radiation safety officer pursuant to 24 RCNY Health Code § 175.10 who shall be delegated authority to ensure the implementation of this radiation protection program.
(d) provide a quality assurance program pursuant to 24 RCNY Health Code § 175.12 for diagnostic and therapeutic uses of radiation-producing equipment operated under applicable provisions of this Article.
(e) for medical centers, hospitals and institutions of higher education, provide for a radiation safety committee to administer the radiation protection program. The radiation safety committee must include the facility operator or a person with the authority to act on behalf of the facility operator, and representation from departments within the facility where radiation sources are used. The committee shall oversee all uses of radiation-producing equipment and radioactive materials within the facility, shall review the activities of the radiation safety officer and shall review the radiation safety program at least annually. The committee, or a subcommittee, shall oversee the administration of the required quality assurance program.
(f) ensure that radiation equipment is used only for those procedures for which it is designed by individuals duly-licensed and fully-qualified to operate such equipment.
(g) ensure that acceptance testing, by a QMP, is performed on all medical and chiropractic diagnostic equipment and radiation therapy treatment and planning equipment before the first use of such equipment on humans; and
(h) at least every 12 months, review the radiation protection program content and its implementation.
(Added City Record 4/24/2019, eff. 5/24/2019)
(a) In addition to those requirements indicated in this section for specific categories, all radiation safety officers must:
(1) demonstrate knowledge of potential radiation hazards and emergency precautions; and
(2) have completed educational courses related to ionizing radiation safety or a radiation safety officer course; and
(3) demonstrate experience in the use and familiarity of the type of equipment used.
(b) Specific duties of the radiation safety officer include, but are not limited to:
(1) establishing and overseeing operating and safety procedures that maintain radiation exposures as low as reasonably achievable (ALARA), and to review them regularly to ensure that the procedures are current and conform with this Article;
(2) ensuring that individual monitoring devices are properly used by occupationally-exposed personnel, that records are kept of the monitoring results, and that timely notifications are made as required by this Article;
(3) investigating and reporting to the Department each known or suspected case of radiation exposure to an individual or radiation level detected in excess of limits established by this Article and each theft or loss of a source of radiation, determining the cause, and taking steps to prevent its recurrence;
(4) having a thorough knowledge of management policies and administrative procedures of the registrant and keeping management informed on a periodic basis of the performance of the registrant's radiation protection program;
(5) assuming control and having the authority to institute corrective radiation control actions, including shut down of operations if necessary, in emergency situations or unsafe conditions;
(6) ensuring that personnel are adequately trained in and complying with this Article, the conditions of the certificate of registration or certified registration, and the operating and safety procedures of the registrant; and
(7) maintaining all records as required by this Article.
(c) For human use radiation equipment installations, the radiation safety officer must be:
(1) a QMP; or
(2) a professional practitioner practicing within the scope of such person's professional practice.
(d) For human use radiation equipment installations requiring a certified registration pursuant to 24 RCNY Health Code § 175.41, the radiation safety officer must be:
(1) a QMP certified by the American Board of Health Physics, the American Board of Radiology or the American Board of Medical Physics in a branch of physics related to the type of use of radiation sources in the installation; or
(2) an authorized user named on the facility's certified registration issued by the Department.
(e) For non-human use radiation equipment installations, the radiation safety officer must be:
(1) a veterinarian for veterinary installations; or
(2) a QMP; or
(3) a person with equivalent training and experience as determined by the Department; or
(4) a researcher or other individual determined by the institution as qualified by training and experience for installations using only x-ray diffraction and fluorescence analysis equipment.
(Added City Record 4/24/2019, eff. 5/24/2019)
Loading...