Loading...
(A) All tanks, regardless of material or method of construction must:
(1) Be watertight;
(2) Be designed and constructed to withstand all lateral earth pressures under saturated soil conditions with the tank empty;
(3) Be designed and constructed with adequate tensile and compressive strength to withstand a minimum of 7 feet of saturated earth cover above the tank top and manhole cover;
(4) Not be subject to corrosion or decay;
(5) Have the manufacturer's name, model number, and tank capacity in gallons permanently displayed on the tank above the outlet pipe;
(6) Not be constructed on-site when saturated soil conditions during construction are closer than 3 inches to the bottom of the excavation;
(7) Be protected against flotation under high water table conditions; and
(8) Have a written and graphic label affixed to maintenance hole covers of sewage tanks warning of the hazardous conditions inside the tanks.
(Prior Code, Ch. 506 § 11.1)
(B) All tanks, regardless of material or method of construction, shall conform to the following criteria:
(1) The liquid depth of any septic tank or compartment thereof shall not be less than 24 inches.
(2) No tank or compartment thereof shall have an inside horizontal dimension less than 24 inches.
(3) Baffles shall be installed at each inlet and outlet of the tank and each compartment.
(4) The space in the tank between the liquid surface and the top of the inlet and outlet baffles shall be not less than 20% of the total required liquid capacity, except that in horizontal cylindrical tanks, this space shall be not less than 15% of the total required liquid capacity.
(5) Inlet and outlet baffles shall be constructed of acid-resistant concrete, acid-resistant fiberglass or plastic not subject to corrosion or decay.
(6) Baffles must be integrally cast with the tank, affixed with a permanent waterproof adhesive, or affixed with stainless steel connectors, top and bottom. Sanitary tees, which are used as baffles, shall be affixed to the inlet or outlet pipes with a permanent waterproof adhesive.
(7) The inlet baffle shall extend at least 6 inches but not more than 20% of the total liquid depth below the liquid surface and at least 1 inch above the crown of the inlet sewer.
(8) The outlet baffle and the baffles between compartments shall extend below the liquid surface a distance equal to 40% of the liquid depth except that the penetration of the indicated baffles or sanitary tees for horizontal cylindrical tanks shall be 35% of the total liquid depth. They also shall extend above the liquid surface as required in division (B)(4) of this section. In no case shall they extend less than 6 inches above the liquid surface. Gas deflecting baffles shall be installed on the outlet of the final septic tank which services an establishment.
(9) The top of the inlet baffle may extend through the top of the tank or maintenance hole cover. The cap must be easily accessible.
(10) In a single compartmented tank, the inlet invert shall be at least 2 inches above the outlet invert.
(11) The inlet and outlet shall be located opposite each other along the axis of maximum dimension. The horizontal distance between the nearest points of the inlet and outlet baffles shall be a least 4 feet.
(12) Inlet baffles, other than sanitary tees, shall be no less than 6 inches or no more than 12 inches from the end of the inlet pipe to the nearest point on the baffle. Outlet baffles, other than sanitary tees, shall be 6 inches measured from beginning of the outlet pipe to the nearest point on the baffle. Sanitary tees used as inlet or outlet baffles shall be at least 4 inches in diameter.
(Prior Code, Ch. 506 § 11.2)
(C) Access to a septic tank shall be as follows:
(1) There shall be 1 or more manholes, at a minimum of 20 inches least dimension, and located within 6 feet of all walls of the tank. The manhole shall extend through the tank cover to a point within 6 inches of finished grade. If the manhole is covered with less than 6 inches of soil, the cover must be secured to prevent unauthorized access.
(2) There shall be an inspection pipe of at least 4 inches in diameter over both the inlet and outlet baffles. The inspection pipe shall extend through the tank cover or the maintenance hole cover, be secured, and be capped flush with or above the finished grade. A downward projection of the centerline of the inspection pipe shall be directed in line with the centerline of the inlet or outlet device.
(3) An inspection pipe at least 4 inches in diameter must be located between the inlet and outlet baffles for the purpose of evaluating the scum and sludge accumulations. The inspection pipe must extend through either the tank cover or manhole cover and must be capped flush with or above finished grade.
(Prior Code, Ch. 506 § 11.3)
(D) A septic tank larger than 3,000 gallons shall be divided into 2 or more compartments.
(1) When a septic tank is divided into 2 compartments, the volume of the first compartment shall be between 1/2 and 2/3 of the total tank volume.
(2) When a septic tank is divided into 3 or more compartments, 1/2 of the total volume shall be in the first compartment and the other half equally divided in the other compartments.
(3) Connections between compartments shall be baffled to obtain effective retention of scum and sludge. The submergence of the inlet and outlet baffles of each compartment must be as specified in division (B)(7) and (8).
(4) Adequate venting shall be provided between compartments by baffles or by an opening of at least 50 square inches near the top of the compartment wall.
(5) Adequate access to each compartment shall be provided by 1 or more maintenance holes, at least 20 inches in dimension, and located within 6 feet of all walls of the tank. The maintenance hole shall extend through the top of the tank compartment cover to a point between 0 and a 6-inch depth below finished grade. If the maintenance hole is between 0 and 6 inches below finished grade, the maintenance hole cover must be secured to prevent unauthorized access.
(Prior Code, Ch. 506 § 11.4)
(E) Where more than 1 tank is used to obtain the required liquid volume, the tanks shall be connected in series. No more than 4 tanks in series can be used to obtain the required liquid volume. The first tank shall be equal to or larger than any subsequent tank in the series.
(Prior Code, Ch. 506 § 11.5)
(F) The outlet pipe extending from the septic tank must not be of cast iron, but must be of sound and durable construction, not subject to corrosion or decay. The outlet pipe must meet the strength requirements of American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), Schedule 40 plastic pipe and must be supported in a manner that there is no deflection during the backfilling and subsequent settling of the soil between the edge of the septic tank and the edge of the excavation. The soil around the pipe must be compacted to at least the original density for a length of 3 feet beyond the edge of the tank excavation.
(Prior Code, Ch. 506 § 11.6)
(G) Any liquid depth which is greater than 78 inches shall not be used when calculating the septic tank capacity. Liquid capacity of septic tanks is described as follows:
(1) For dwellings there shall be 2 septic tanks in series with the liquid capacity based on the number of bedrooms contemplated in the dwelling; such tanks shall be at least as large as the capacities in Table II. The only exception to this requirement is for the upgrade of an existing conforming system if the primary tank capacity is met and there is no garbage disposal or sewage pump. System replacement shall require 2 tanks in series.
Number of Bedrooms | Tank Liquid Capacities (Gallons) |
2 or less | 1,000 and 500 |
3 or 4 | 1,000 and 1,000 |
5 or 6 | 1,500 and 1,000 |
7, 8, and 9 | 2,000 and 1,000 |
10 or more | Septic tank shall be sized as an other establishment with the second tank in series at least 50% of the capacity of the first tank |
Multiple-family dwelling containing 2 or more units | Size shall be the sum of the individual dwelling unit requirements |
(2) The liquid capacity of septic tanks serving other establishments shall be sufficient to provide a sewage detention period of not less than 36 hours in the tank for maximum design flows of less than 1,500 gallons per day, but in no instance shall the liquid capacity be less than 750 gallons. For maximum design flows greater than 1,500 gallons per day, the minimum liquid capacity shall equal 1,125 gallons per day plus 75% of the maximum design flow.
(a) For restaurants and laundromats, twice the liquid capacity detailed above must be provided.
(b) For laundromats, the outlet baffle of the septic tank must be submerged to a depth of 50%.
(Prior Code, Ch. 506 § 11.7)
(H) A sewage pump must not deliver sewage to a 1-tank system if the pump cycle delivers more than 1% of the liquid capacity of the tank. For systems with multiple tanks, at least 2 tanks in series must be used, each having at least the liquid capacity specified in this section. The volume of sewage delivered in each pump cycle must not exceed 5% of the liquid capacity of the first tank.
(Prior Code, Ch. 506 § 11.8)
(I) The sewage tank shall be placed so that it is easily accessible for the removal of liquids and accumulated solids. The soil cover over a tank shall not exceed 5 feet. The sewage tank shall be placed on firm and settled soil capable of bearing the weight of the tank and its contents. Sewage tanks shall be set back as specified in Table III, below. Sewage tanks shall not be placed in areas subject to flooding or in floodplains delineated by local regulations adopted in compliance with Minn. Rules, Chapter 6120, as it may be amended from time to time, or in areas for which regional flood information is available from the DNR, except that in areas where 10-year flood information is available from and/or approved by the DNR, sewage tanks may be installed as an alternative system in accordance with all provisions of § 157.39(C).
Minimum Setback Distances (Feet) | ||
Feature | Sewage Tank | Soil Treatment Area |
Water supply well less than 50 feet deep and not encountering at least 10 feet of impervious material | 50 | 100 |
Any other water supply well or buried water suction pipe | 50 | 50 |
Buried pipe distributing water under pressure | 10 | 10 |
Occupied buildings and buildings with basements or crawl spaces | 10 | 20 |
Non-occupied structures | 5 | 10 |
Property lines | 10* | 10* |
Above-ground swimming pools | 10 | 10 |
In-ground swimming pools | 10 | 10 |
The Ordinary High Water Mark of: | ||
Natural environment lakes and streams | 150* | 150* |
Recreation development lakes and streams | 75* | 75* |
General development lakes and streams | 75* | 75* |
All unclassified waters | 75* | 75* |
St. Croix River Rural Districts | 150* | 150* |
St. Croix River Urban Districts | 100* | 100* |
Blufflines: | ||
St. Croix River blufflines | 40* | 40* |
Shoreland and blufflines | 20* | 20* |
* These standards may be modified through the variance process. | ||
(Prior Code, Ch. 506 § 11.9) (Am. Ord. 7489, passed 5-16-2000)
(J) Aerobic tank treatment systems shall comply with the general requirements for sewage tanks set forth in this chapter, and with the following:
(1) The treatment system including each individual unit or compartment shall be easily accessible for inspection and maintenance and shall be provided with secured covers.
(2) Aerobic tanks shall comply with National Sanitation Foundation (NSF) Standard No. 40 (November 1990) which is incorporated by reference. Effluent quality shall meet or exceed NSF Class II standards.
(3) No additional reduction in soil treatment or absorption area shall be allowed with the use of an aerobic tank.
(4) An effective maintenance contract, approval by the permitting authority, shall be maintained at all times.
(Prior Code, Ch. 506 § 11.10)
(A) Frost protection. Supply pipes must be protected from freezing where the pipe passes under driveways, sidewalks, roadways, or other areas where deep frost penetration is expected.
(Prior Code, Ch. 506 § 12.1)
(B) Gravity distribution.
(1) Serial distribution must be used to distribute effluent to individual trenches in a soil treatment system unless the necessary elevation differences between trenches for drop boxes cannot be achieved by natural topography or by varying the excavation depths, in which case parallel distribution shall be used. If drop boxes are used, they must meet the following standards:
(a) The drop box shall be watertight and constructed of durable materials not subject to corrosion or decay.
(b) The invert of the inlet pipe shall be at least 1 inch higher than the invert of the outlet pipe to the next drop box.
(c) The invert of the outlet pipe to the next trench shall be no greater than 2 inches higher than the crown of the outlet pipe of the trench in which the box is located.
(d) When sewage tank effluent is delivered to the drop box by a pump, the pump discharge shall be directed against a wall or side of the box on which there is no outlet.
(e) The drop box shall be covered by a minimum of 6 inches of soil and it shall be placed on firm and settled soil.
(f) An inspection pipe at least 4 inches in diameter must be provided and capped flush with or above finished grade.
(2) Systems using valve boxes shall comply with the following requirements:
(a) The valve boxes shall be watertight and constructed of durable materials not subject to corrosion or decay.
(b) The invert of the inlet pipe shall be at least 1 inch higher than the inverts of the outlet pipes to the trenches.
(c) When sewage tank effluent is pumped to a valve box, either a baffle wall must be installed in the valve box or the pump discharge must be directed against a wall or side of the box on which there is no outlet. The baffle must be secured to the box and extend at least 1 inch above the crown of the inlet pipe.
(d) The valve box shall be covered by a minimum of 6 inches of soil and it shall be placed on firm and settled soil.
(e) An inspection pipe at least 4 inches in diameter must be provided and capped flush with or above the finished grade.
(3) Distribution boxes must meet the following standards:
(a) The box must be watertight and must be constructed of durable materials not subject to corrosion or decay.
(b) The distribution box shall be covered by a minimum of 6 inches of soils and it shall be placed on firm and settled soil. An inspection pipe must be provided and capped flush with or above the finished grade.
(c) The inverts of all outlets must be set and maintained at the same elevation.
(d) The inlet invert must be either at least 1 inch above the outlet inverts or be sloped such that an equivalent elevation above the outlet invert is obtained within the last 8 feet of the inlet pipe.
(e) Each drainfield trench line must be connected separately to the distribution box and must not be subdivided. Distribution boxes must be connected to one another if each box has distribution pipes.
(f) When sewage tank effluent is delivered by pump, either a baffle wall must be installed in the distribution box or the pump discharge must be directed against a wall or side of the box on which there is no outlet. The baffle must be secured to the box and must extend at least 1 inch above the crown of the inlet pipe.
(4) (a) Distribution pipes used in trenches or beds for gravity distribution must be at least 4 inches in diameter and must be constructed of sound and durable material not subject to corrosion or decay or to loss of strength under continuously wet conditions. Distribution pipes must have a load bearing capacity of not less than 1,000 pounds per lineal foot.
(b) Distribution pipes used for gravity distribution must have 1 or more rows of holes of no less than 1/2 inch in diameter spaced no more than 40 inches apart. Holes must be spaced to prevent failure due to loads.
(c) The distribution pipe for gravity distribution must be laid level or on a uniform slope away from the distribution device of no more than 4 inches per 100 feet.
(d) Gravity distribution pipes in seepage beds must be uniformly spaced no more than 5 feet apart and not more than 30 inches from the side walls of the seepage bed.
(Prior Code, Ch. 506 § 12.2)
(C) Pressure distribution.
(1) Pressure distribution must be used for the following soil treatment systems:
(a) All mound systems;
(b) All at-grade systems; and
(c) Systems where the soil percolation rate is 0.1 to 5 minutes per inch if the effluent is pumped to a seepage bed or to trenches that are all at the same elevation.
(2) Distribution pipes used for pressure distribution must be constructed of sound and durable material not subject to corrosion or decay or to loss of strength under continuously wet conditions.
(3) All pipes and associated fittings used for pressure distribution must be properly joined together. The pipe and connections must be able to withstand a pressure of at least 40 pounds per square inch.
(4) Perforations must be no smaller than 3/16-inch diameter and no larger than 1/4-inch diameter. The number of perforations, perforation spacing and pipe size for pressure distribution laterals must be as shown in Table IV. The friction loss in any individual perforated lateral must not exceed 20% of the average head pressure on the perforations.
Maximum Allowable Number of 1/4-Inch Diameter, or Smaller Perforations per Lateral
| ||||
Perforation Spacing in Feet
|
Pipe Diameter - Normal and Inside
| |||
(5) Perforation holes must be drilled straight into the pipe and not at an angle. The perforated pipe laterals must be installed level with the perforations downward. Perforation holes must be free of burrs.
(6) Laterals must be spaced no further than 60 inches apart in seepage beds and mound rock beds and must be spaced no further than a horizontal distance of 30 inches from the outside edge of a drainfield rock layer.
(7) Laterals must be connected to a header or manifold pipe that is of a diameter such that the friction loss in the header or manifold will be no greater than 5% of the average head at the perforations. The header or manifold pipe must be connected to the supply pipe from the pump.
(8) Perforated laterals must be designed and installed in such a way that no perforations are located closer than 12 inches from the edge of the drainfield rock.
(Prior Code, Ch. 506 § 12.3)
(A) General requirements. A dosing device is not necessary in all situations but, where used, shall comply with the following requirements.
(1) The dosing chamber shall be watertight and constructed of sound and durable materials not subject to excessive corrosion or decay, vented, and must be designed and constructed to withstand lateral pressures when the tank is empty.
(2) There shall be 1 or more maintenance holes, at least 20 inches least dimension and located directly above the dosing device. The maintenance hole shall extend through the dosing chamber cover to final grade and shall be so constructed as to prevent unauthorized entry.
(3) The dosing chamber shall either include an alternating 2-pump system or have a minimum capacity of 500 gallons or 100% of the average design flow, whichever is greater.
(4) A dosing device must employ an alarm device to warn of failure.
(5) Pumps shall be elevated from the bottom of the dosing chamber to protect the pump from settled solids. The pump, pump controls, and pump discharge line shall be installed so as to be accessible for servicing without entering the dosing chamber.
(6) Electrical installations shall comply with applicable laws and ordinances including the latest codes, rules, and regulations of public authorities having jurisdiction and with
(B) Dosing device for gravity distribution.
(1) Where a dosing device is employed, a pump or siphon shall deliver the dose to the soil treatment system for gravity distribution over the soil treatment area.
(2) For dwellings, the dosing device shall discharge at least 600 gallons per hour, but no more than 2,700 gallons per hour.
(3) For other establishments, the dosing device should discharge at a rate at least 10% greater than the water supply flow rate but no faster than the rate at which effluent will flow out of the distribution device.
(4) If the dosing device is a siphon, a maintenance inspection shall be made every 6 months by the owner or the owner's agent. The siphon shall be maintained in proper operating condition.
(5) If the dosing device is a pump, it shall be cast iron or bronze fitted and with stainless steel screws or constructed of other sound, durable, and corrosion-resistant materials.
(6) Where the soil treatment area is at a higher elevation than the pump, sufficient dynamic head shall be provided for both the elevation difference and friction loss.
(7) Where the dosing device is a pump, an alarm device shall be installed to warn of pump failure.
(Prior Code, Ch. 506 § 13.2)
(C) Dosing devices for pressure distribution.
(1) The dosing device shall be a pump which is cast iron or bronze fitted and with stainless steel screws or constructed of sound, durable, and corrosion-resistant materials.
(2) The pump discharge capacity shall be based upon the perforation discharges for an average head of 1.0 foot for dwellings and 2.0 feet for other establishments. Perforation discharge will be determined by the following formula:
q = 19.65 cd ²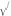 h
h
where: q = discharge in gallons per minutes;
c = 0.60 = co-efficient of discharge;
d = perforation diameter in inches; and
h = head in feet
(3) The pump discharge head shall be a least 5 feet greater than the head required to overcome pipe friction losses and the elevation difference between the pump and the distribution device.
(4) The quantity of effluent delivered for each pump cycle shall be no greater than 25% of the average design flow.
(5) A siphon will not be allowed as a dosing device to deliver effluent to a pressure distribution system.
(6) An alarm device shall be installed to warn of pump failure.
(Prior Code, Ch. 506 § 13.3)
Loading...