(B) Purpose and intent. The purpose and intent of this section is to establish standards and procedures by which the installation and operation of wind and solar energy system shall be governed within the city. The city finds that it is in the public interest to encourage alternative energy systems that have a positive impact on energy production and conservation while not having an adverse impact on the community.
ACCESSORY. A system designed as a secondary use to existing buildings or facilities, wherein the power generated is used primarily for on-site consumption.
ALTERNATIVE ENERGY SYSTEM. A wind energy conversion system or a solar energy system.
BUILDING-INTEGRATED SOLAR ENERGY SYSTEM. A solar energy system that is an integral part of a principal or accessory building, rather than a separate mechanical device, replacing or substituting for an architectural or structural component of the building including, but not limited to, photovoltaic or hot water solar systems contained within roofing materials, windows, skylights and awnings.
CLOSED LOOP GROUND SOURCE HEAT PUMP SYSTEM. A system that circulated a heat transfer fluid, typically food-grade antifreeze, through pipes or coils buried beneath the land surface or anchored to the bottom of a body of water.
FLUSH-MOUNTED SOLAR ENERGY SYSTEM. A roof-mounted system mounted directly abutting the roof. The pitch of the solar collector may exceed the pitch of the roof up to 5% but shall not be higher than ten inches above the roof.
GROUND SOURCE HEAT PUMP SYSTEM. A system that uses the relatively constant temperature of the earth or a body of water to provide heating in the winter and cooling in the summer. System components include open or closed loops of pipe, coils or plates; fluid that absorbs and transfers heat; and a heat pump unit the processes heat for use or disperses heat for cooling; and an air distribution system.
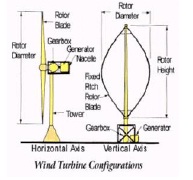
HORIZONTAL AXIS WIND TURBINE. A wind turbine design in which the rotor shaft is parallel to the ground and the blades are perpendicular to the ground.
HUB. The center of a wind generator rotor, which holds the blades in place and attaches to the shaft.
HUB HEIGHT. The distance measured from natural grade to the center of the turbine
hub.
MONOPOLE TOWER. A tower constructed of tapered tubes that fit;together symmetrically and are stacked one section on top of another and bolted to a concrete foundation without support cables.
PASSIVE SOLAR ENERGY SYSTEM. A system that captures solar light or heat without transforming it to another form of energy or transferring the energy via a heat exchanger.
PHOTOVOLTAIC SYSTEM. A solar energy system that converts solar energy directly into electricity.
RESIDENTIAL WIND TURBINE. A wind turbine of ten kilowatt (kW) nameplate generating capacity or less.
SMALL WIND TURBINE. A wind turbine of 100 kW nameplate generating capacity or
less.
SOLAR ENERGY SYSTEM. A device or structural design feature, a substantial purpose of which is to provide daylight for interior lighting or provide for the collection, storage and distribution of solar energy for space heating or cooling, electricity generation or water heating.
TOTAL HEIGHT. The highest point above natural grade reached by a rotor tip or any other part of a wind turbine.
TOWER. A vertical structure that supports a wind turbine.
UTILITY WIND TURBINE. A wind turbine of more than 100 kW nameplate generating capacity.
VERTICAL AXIS WIND TURBINE. A type of wind turbine where the main rotor shaft runs vertically.
WIND ENERGY CONVERSION SYSTEM (WECS). An electrical generating facility that consists of a wind turbine, feeder line(s), associated controls and may include a tower.
WIND TURBINE. Any piece of electrical generating equipment that converts the kinetic energy of blowing wind into electrical energy through the use of airfoils or similar devices to capture the wind.