(A) Definitions. For purposes of this section the following definitions shall apply unless the context clearly indicates or requires a different meaning.
BRICK. Manufactured of clay and shale masonry units. Primary raw materials include surface clays, fire clays, shales, or combinations of these. Units are formed by extrusion, molding or dry-pressing and are fired in a kiln at temperatures between 1800° Fahrenheit and 2100° Fahrenheit (980° Celsius and 1150° Celsius). Units include a range of colors, textures, sizes, and physical properties. Material standards for brick and structural clay tile include: ASTM C216 (facing brick), ASTM C62 (building brick), ASTM C652 (hollow brick), ASTM C212 (structural clay facing tile), and ASTM C34 (structural clay load-bearing tile).
BUILDING HEIGHT. The vertical distance on a building, measured from the average elevation of the finished grade within 20 feet of the structure to the highest point on the roof.
CONCRETE MASONRY UNITS. Hollow and solid load bearing and non-load bearing units made from Portland cement, water, and mineral aggregate. CONCRETE MASONRY UNITS manufactured under this specification shall conform to the specified density classifications and compressive strength requirements of ASTM C90 standards.
DECORATIVE CONCRETE MASONRY UNITS. Includes concrete masonry units with finished surfaces, including burnished, split faced, indented, hammered, fluted, ribbed or similar architectural finish; coloration shall be integral to the masonry material and shall not be painted on; minimum thickness of three and five-eighths inches when applied as a veneer; shall include light weight and featherweight concrete block or cinder block units.
MASONRY MATERIALS. Includes that form of construction defined below and composed of clay brick, stone, decorative concrete block, rock or other materials of equal characteristics laid up unit by unit set in mortar.
NONRESIDENTIAL BUILDINGS. Those buildings utilized for use other than single-family, two-family and multiple family dwelling related to accessory use as a primary non-residential building.
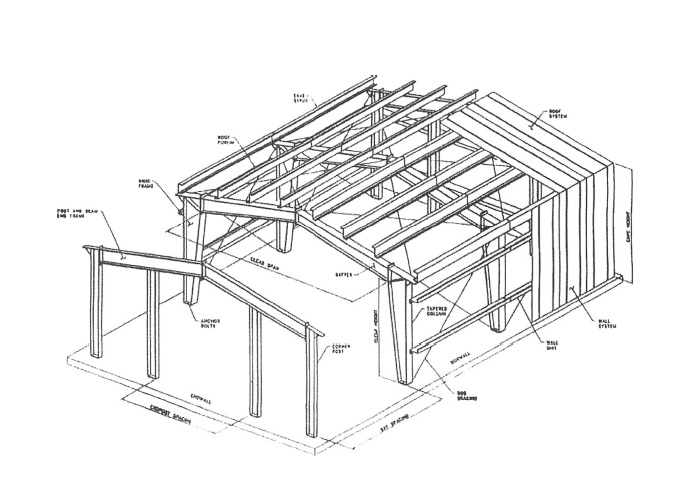
POST FRAME BUILDING CONSTRUCTION. A post frame building is characterized by primary structural frames of posts as columns and trusses or rafters as roof framing. Post framed construction shall include steel, light-gauge metal and wood constructions. The roof framing is attached to the posts, either directly or indirectly through structural headers. Posts are embedded in the soil and supported by isolated footings, or are attached at the top of piers, concrete or masonry walls, slabs-on-grade, or other suitable foundations. Secondary framing members, purlins in the roof and girts in the walls, are attached to the primary framing members to provide lateral support and to transfer sheathing loads, both in-plane and out-of-plane, to the posts and roof framing. Structures are sheathed with a wide variety of materials. See the below diagram for this type of construction
PRECAST CONCRETE PANELS. Includes reinforced concrete systems, fabricated off-site and installed on-site. Precast systems shall be structural systems and shall be covered by defined masonry materials that can be laid up unit by unit set in mortar and meet the required percentage of coverage as defined in this chapter.
RESIDENTIAL BUILDINGS. Those buildings utilized for a single-family, two-family, and multiple family dwelling, related to accessory use as a primary residential unit.
STONE. Includes naturally occurring granite, marble, limestone, slate, river rock, and other similar hard and durable all weather stone that is customarily used in exterior building construction; may also include cast or manufactured stone product, provided that such product yields a highly textured stonelike appearance, its coloration is integral to the masonry material and shall not be painted on. and it is demonstrated to be highly durable and maintenance free; natural or manmade stone shall have a minimum thickness of two and five-eighths inches when applied as a veneer.
UNACCEPTABLE EXTERIOR MATERIALS. The following materials shall not qualify nor be defined as MASONRY CONSTRUCTION in meeting the minimum requirements for exterior construction of buildings:
(a) Stucco, exterior plaster, adobe or mortar wash surface material;
(b) Exterior insulation and finish systems (EIFS) such as Dryvit, acrylic matrix, synthetic plaster, or other similar synthetic material;
(c) Cementitious fiber board siding (such as "Hardy Plank" or "Hardy Board").
(B) Exterior construction requirements.
(1) Residential construction standards.
(a) All principal and accessory buildings located in the multi-family (MF) and R-4 residential zoning districts shall have at least 30% of the total exterior walls, excluding doors and windows, constructed of brick, stone, or a combination of both materials. Stucco and/or exceptions to the above requirements may be considered by the Plan Commission on case-by-case basis.
1. The structure shall have a change of roof plane, gable, or dormer on both the front and the rear for each dwelling unit. Units that are on corners shall have same for all sides that face a public street.
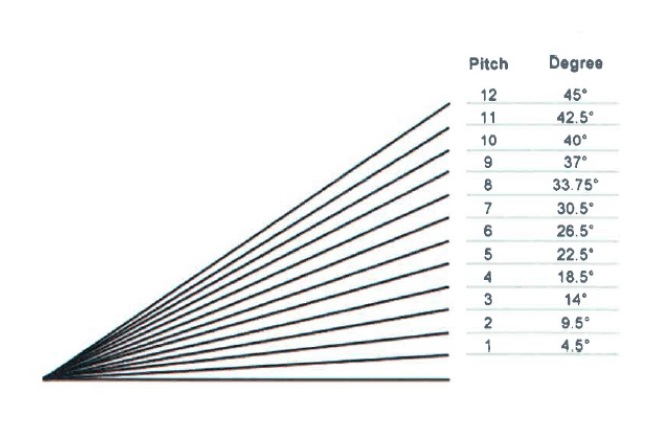
2. Sloped roof pitch shall not be less than 8/12 on the primary roof and less than 3/12 on lesser roofs.
(b) Single-family residential construction requirements.
1. Dwelling units/homes with 2,000 square feet of finished living space or less must have masonry coverage of at least 25% on the front facade, constructed of brick, stone, or a combination of both materials. Stucco and/or exceptions to the above requirements may be considered by the Zoning Administrator on a case-by-case basis.
2. Dwelling units/homes must have overhanging eaves of at least 12 inches in length.
3. Dwelling units/homes must have variation on the front facade elevation via changes in roofline and bump-outs.
4. For dwelling units/homes on corner lots, each facade facing a public or private street shall be treated as a front facade.
(2) Non-residential construction standards. The following standards apply to all new non-residential building construction and any building expansion of 25% or more in floor area or a significant change in use of the building from one occupancy to another occupancy in accordance with the established building codes:
(a) All non-residential buildings shall be constructed of exterior fire-resistant construction having at least 80% of the total exterior walls excluding doors and windows, constructed of severe weather rated brick, stone, split faced concrete textured surface block or glass wall construction, in accordance with the town's Building Code and Fire Prevention Code.
(b) Building front and side facades or any portion that has exposure to a public or private street, residential zoning districts, or any public exposure, including parking lot exposure for pad sites and freestanding buildings, shall be constructed entirely 100% of severe weather rated stone, brick, or glass wall construction. Strict adherence to this rule shall not be such as to prevent architectural creativity. Other materials or a combination of severe weather rated brick, stone and other materials may be considered based on architectural creativity by the Plan Commission.
(c) Metal buildings and steel post frame or wood post frame building construction is prohibited in all commercial zoning districts.
(d) Building materials.
1. Each building elevation shall provide architectural features such as columns, reveals, articulations, or changes in building materials, architectural styles or ornamentation and color to break up long facades exceeding 20 feet.
2. All buildings shall be designed with a minimum of six external corners, in order to eliminate the impact of box-looking design for the buildings. Corners created as a result of the placement of doors and windows do not count towards this total.
3. Building exteriors shall exhibit variation in design and view of the structure. A minimum of three materials shall be used for building exteriors.
4. Exposed concrete, smooth surface concrete block, or metal finishes shall not be permitted in non-residential zoning districts unless approved as part of the design by waiver approval.
5. EIFS may generally be used as accent material for window head, sill or cornices around the building. EIFS shall not be permitted as a primary building material.
(e) Roofs.
1. Sloped roofs shall be composed of standing rib (standing seam) or dimensional shingles in a color that matches the building and surrounding commercial district.
2. Sloped roof planes shall be broken up with changes of plane, or gables or dormers.
3. Sloped roof pitch shall not be less than 6/12.
4. The roof shall be a key architectural element of the building designed to express the building and to promote the overall scale and character of the district.
5. The roof form of new construction shall have a recognizable "top" and vary with modern expressions of parapets, gables, overhanging eaves, chimneys, brackets, and cornices.
6. All rooftop mechanicals including, but not limited to HVAC must be screened from view.
7. A waiver may be granted to correspond with the design theme and overall aesthetics that a development/building is attempting to achieve by the Plan Commission during the commercial development plan review/approval process outlined in this chapter.
(f) Entryways. Entryways shall use creative entry treatments and focal points such as canopies, awnings, cornice treatments, or atriums.
(g) Carports constructed entirely out of metal are not permitted. Carports shall be compatible in design and material with the main structure.
(h) Parking lots.
1. Parking lots shall be designed to provide coordinated access to parking areas on adjoined tracts or parcels.
2. New access points onto main thoroughfares shall be coordinated with existing access points to the extent possible.
3. All parking areas and drives shall be paved with asphalt or concrete. Brick pavers or other decorative pavements may be used as accents in parking area design. Cast-in-place concrete curbs shall be installed.
(i) Requirements for large industrial buildings.
0 - 50,000 sq. ft. | 75% brick or stone veneer on all sides of the building(s) |
50,001 - 100,000 sq. ft. | 50% brick or stone veneer on all sides of the building(s) |
100,001 sq. ft. and larger | 25% brick or stone veneer on front facade and side facade if siding on a street. |
(3) Waivers.
(a) Exceptions to these requirements may be considered by the Plan Commission based upon the following:
1. Architectural design and creativity;
2. Compatibility with surrounding developed properties.
(b) The Plan Commission, upon application duly filed by the applicant, may grant a waiver from the terms of this section, as amended from time to time, and the requirements set forth herein during the commercial development plan review/approval process upon affirmative vote of the Plan Commission acting on such waiver application. The application for a waiver shall set forth in specific language the grounds or reasons upon which such a waiver request is being made.
(c) The terms and conditions of the waiver, if approved, shall be set forth in the minutes of the meeting.
(C) Nonconforming buildings. Where a lawful building exist at the effective date of the adoption or amendment of this chapter and said building could not be built under the terms of this section, it may continue so long as it remains lawful, subject to the following provisions:
(1) Such a building may not be enlarged by more than 25% of its existing foundation footprint unless the entire building is brought into conformance with the terms and requirements of this section.
(2) The exterior walls of such a building may not be modified, altered, or enlarged in a way which increases its nonconformity unless the modification, alteration, or enlargement is in conformance with the provisions of this section.
(3) In the event that a building is destroyed by any means to an extent more than 50% of its replacement cost at the time of destruction, it shall not be reconstructed except in conformance with the provisions of this section.
(D) Penalties. Any person, firm or corporation that violates, disobeys, omits, neglects, or refuses to comply with, or who resist in the enforcement of any of the provisions of this section, as amended, shall be fined $250 for each offense. Each day that a violation exists shall constitute a separate offense. The penalty should not be construed as exclusive, and the town hereby provides that any other remedy available to it. in law or in equity, may be utilized and implemented in the enforcement of this section.
(Ord. 210, passed 9-11-2012; Am. Ord. 210-A, passed 12-10-2015; Am. Ord. 191-A, passed 12-8-2020)